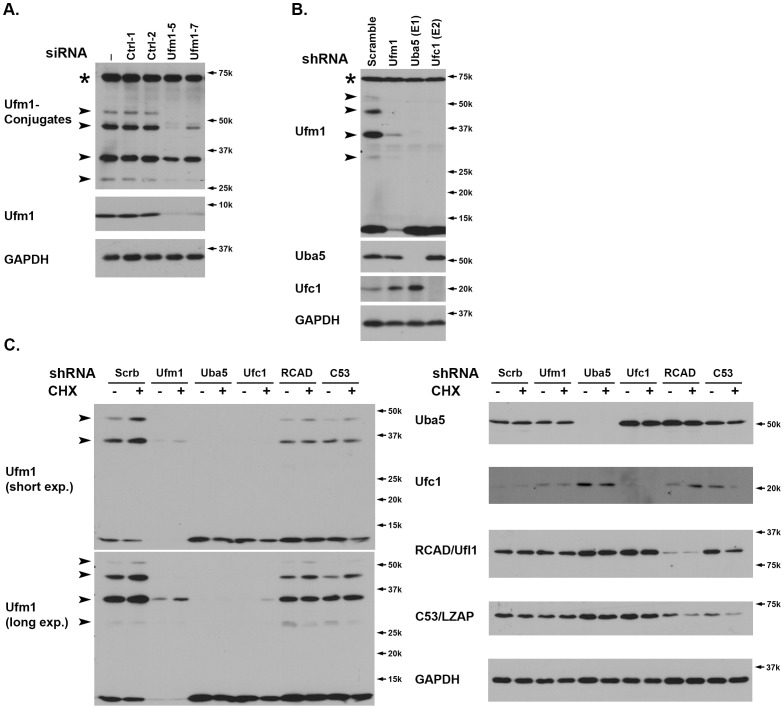
Figure 1. RCAD/Ufl1 and its binding partner C53/LZAP were involved in ufmylation of endogenous Ufm1 targets.
A. The endogenous Ufm1 conjugates. HCT116 cells were transiently transfected with siRNAs, and the cell lysates were collected two days after transfection and subject to WB using Ufm1 antibody. Specific Ufm1 conjugates were marked by arrowheads, and Ufm1 knockdown efficiency was evaluated by Ufm1 immunoblotting. A “70 kD” non-specific band marked by “*”. B. Ufmylation of endogenous targets was reduced by shRNA-mediated knockdown of Ufm1, Uba5 and Ufc1. HCT116 cells were infected with lentiviral vectors expressing specific Ufm1, Uba5 and Ufc1 shRNAs. The cells were selected with puromycin and the cell lysates were collected after 4-day incubation. Knockdown of specific genes were confirmed by immunoblotting of specific antibodies, respectively. The Ufm1 conjugates were marked by arrowheads. C. RCAD/Ufl1 and its binding partner C53/LZAP were involved in ufmylation of endogenous Ufm1 targets. HCT116 cells were infected with specific lentiviral shRNAs as indicated, and knockdown of corresponding genes was confirmed by immunoblotting. Scramble shRNA was used as the negative control. After 4-day selection and incubation, the cells were treated with cycloheximide (CHX, 10 µg/ml) for 6 hours, and the cell lysates were collected and subject to immunoblotting.