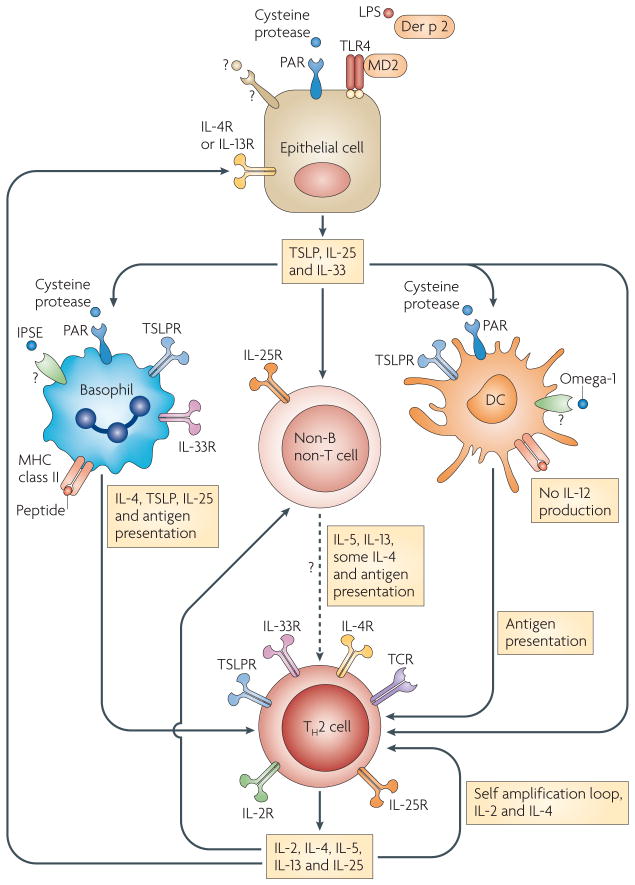
Figure 2. Cytokines have crucial roles in the initiation and amplification of TH2-type immune responses.
Cysteine protease- and/or lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-containing allergens, as well as helminth products, can activate lung and intestinal epithelial cells to produce thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), interleukin-25 (IL-25) and IL-33, which initiate T helper 2 (TH2)-type immune responses by acting on basophils, dendritic cells (DCs) and/or non-B non-T cells. The allergen Der p 2 is structurally homologous to MD2, a component of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signalling complex. A high dose of Der p 2 enhances allergic inflammation in a TLR4-dependent MD2-independent manner. Some cysteine proteases and helminth products, such as IL-4-inducing principle of Schistosoma mansoni eggs (IPSE), can also directly stimulate basophils to produce TSLP and IL-4. Omega-1, a component of S. mansoni egg antigen, modulates DC function to favour a TH2 cell promoting phenotype. Basophils, DCs and possibly other cells can serve as antigen-presenting cells to drive TH2 cell differentiation under the influence of various cytokines such as TSLP, IL-4 and IL-25. Cytokines produced by TH2 cells, including IL-2, IL-4 and IL-25, can self-amplify the differentiation process. At the effector stage, TH2 cells and epithelial cells may further amplify TH2-type responses through a cytokine-mediated positive regulatory loop. Although they are not shown in the figure, other immune cells, including natural killer (NK) cells, NKT cells, γδ T cells, macrophages, B cells, eosinophils and mast cells, may also participate in the initiation and amplification of TH2-type responses by creating a TH2-biased cytokine environment. In addition, IL-4 may induce IL-12 production by DCs105 or kill TH2-inducing DCs106, suggesting there are also negative regulatory mechanisms for TH2-type immune responses. PAR, protease-activated receptor; R, receptor; TCR, T cell receptor.