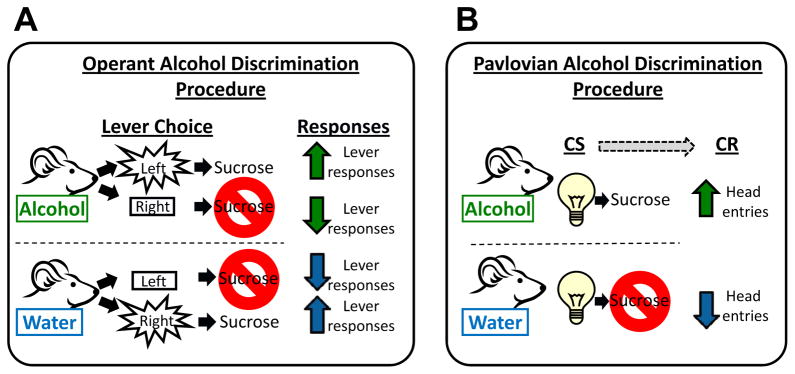
Figure 1. Illustration of drug discrimination procedures.
(A) In the operant drug discrimination procedure, on alcohol training sessions, alcohol sets the occasion for which responses on the left lever result in sucrose delivery; responses on right lever have no consequences. This leads to an increase in alcohol-appropriate (i.e., left) lever responses. On water training sessions, responses on the right lever result in sucrose delivery; responses on the left lever have no consequences. This lead to an increase in water-appropriate (i.e., right) lever responses. (B) In the Pavlovian drug discrimination procedure, on alcohol sessions, alcohol sets the occasion for which the offset of a light (conditioned stimulus; CS) will be followed by sucrose delivery, which leads to an increase in head entries (conditioned response; CR) during the light. On water sessions, no sucrose is delivered following light offset, which lead to a decrease in head entries during the light CS.