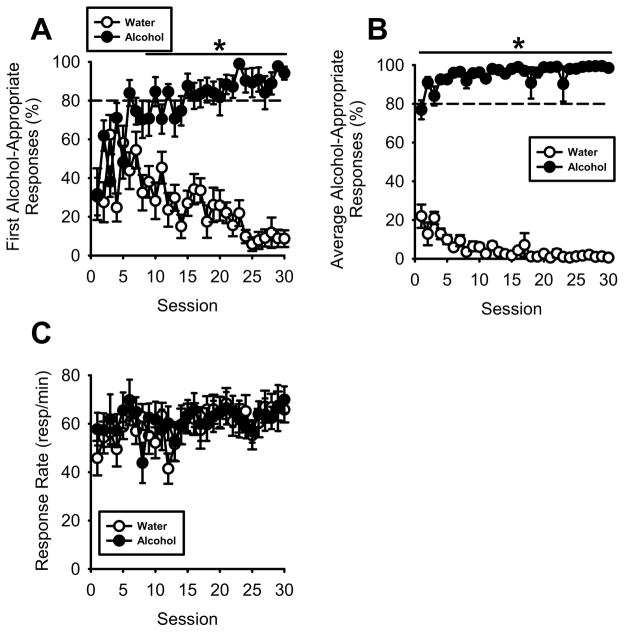
Figure 4. Acquisition of the alcohol discrimination using operant procedures.
(A) Across training sessions, alcohol-appropriate responses after completion of the first FR10 requirement (i.e., prior to the first sucrose delivery) increased during alcohol (1 g/kg, IG) sessions and decreased during water sessions. By session 6, alcohol-appropriate responses were significantly higher during alcohol sessions than water sessions. By session 15 alcohol-appropriate responses were consistently ≥80% after alcohol administration and consistently ≤20% after water administration by session 24. (B) Average alcohol-appropriate responses during alcohol sessions were significantly greater than water sessions throughout training, which reflects, in part, influence of reinforcer delivery. (C) Response rate (responses/min) did not vary between alcohol and water sessions.