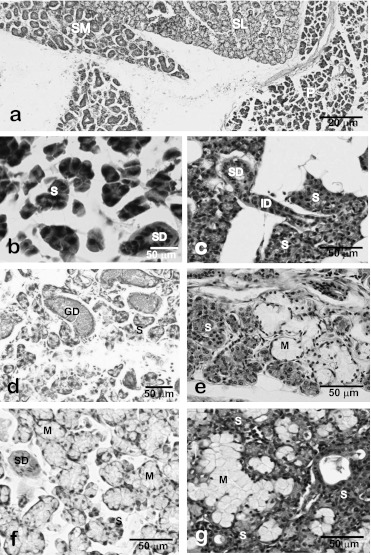
Fig. 5.
Light micrographs of major salivary glands of the rat (a, b, d, f) and human (c, e, g). Major salivary glands of rats are easily distinguishable light-microscopically by the histological features of acinar and ductal structures (a). In rat (b) and human (c) parotid glands, acini are composed of serous (or seromucous) cells. In rat submandibular glands (d), the granular ducts (GCT) are markedly developed but mucous acini and serous demilunes are not recognized. In human submandibular glands (e), mixed acini accompanying serous demilunes are observed whereas no GCT portions are found. In rat (f) and human (g) sublingual glands, mixed acini accompanying the serous demilunes are observed. P, parotid gland; SL, sublingual gland; SM, submandibular gland; S, serous acini; M, mucous acini; SD, striated duct; ID, intercalated duct; GD, granular duct; D, demilune.