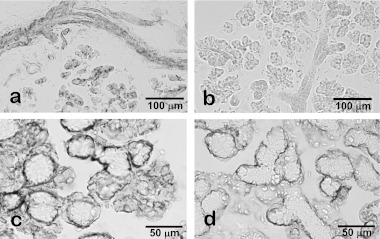
Fig. 6.
Non-specific immunoreactions in the rodent salivary glands. Without specific primary antibodies anti-mouse IgG secondary antibody reacted with duct cells and luminal membrane of acinar cells in rat parotid glands (a) whereas no non-specific reaction was detected by using pre-absorbed secondary antibody for rat tissues (b). The immunohistochemical procedure for the rat sublingual glands by the combination of an anti-smooth muscle actin mouse monoclonal antibody, an established marker for myoepithelial cells, and conventional anti-mouse IgG antibody triggers a broader immunoreaction than expected, including serous demilunes (c). After replacing the secondary antibody with the pre-absorbed one for rat tissue, the immunoreaction is confirmed to localize in myoepithelial cells (d).