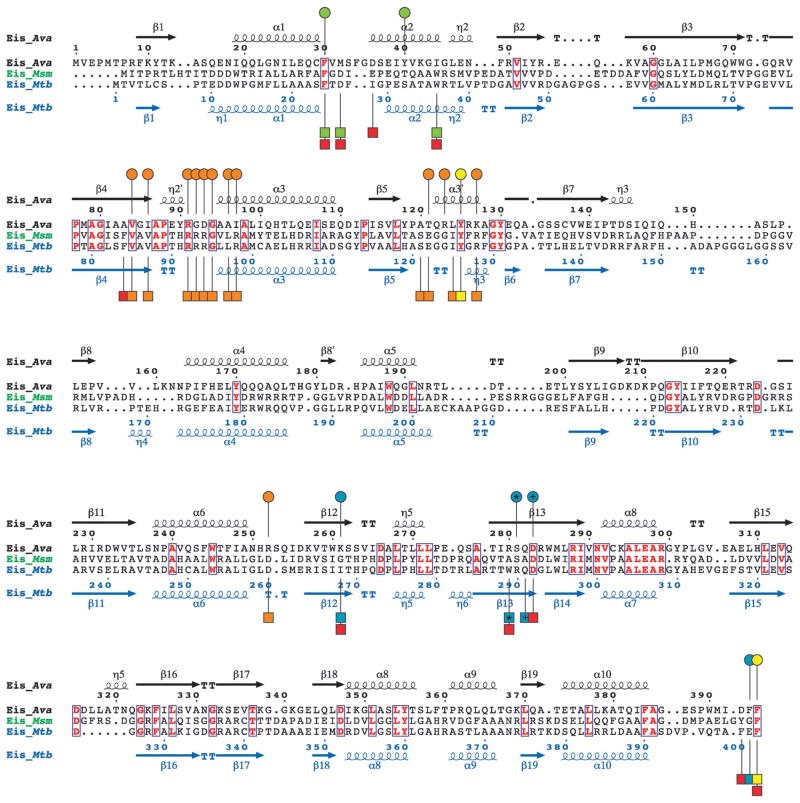
Fig. 2.
Structure-based sequence alignment of Eis_Ava from A. variabilis ATCC 29413, Eis_Msm from M. smegmatis str. MC2 155, and Eis_Mtb from M. tuberculosis H37Rv generated using Secondary-structure matching (SSM).9 Residues in bold red in blue boxes are conserved between the 3 Eis homologues. The circles above and the squares below the Eis_Ava and Eis_Mtb sequences, respectively, correspond to important residues in these sequences. Based on structural and mutagenesis studies of Eis_Mtb, the residues proposed to be involved in catalysis, in AcCoA binding, and in the formation of the AG-binding pocket are marked by yellow, orange, and red circles/squares, respectively.3 The AG-binding pocket of Eis_Mtb is divided into two channels. Residues lining these two channels are marked by green and turquoise circles/squares. The * and the + symbols indicate residues that structurally aligned when superimposing the crystal structures of Eis_Ava and Eis_Mtb.