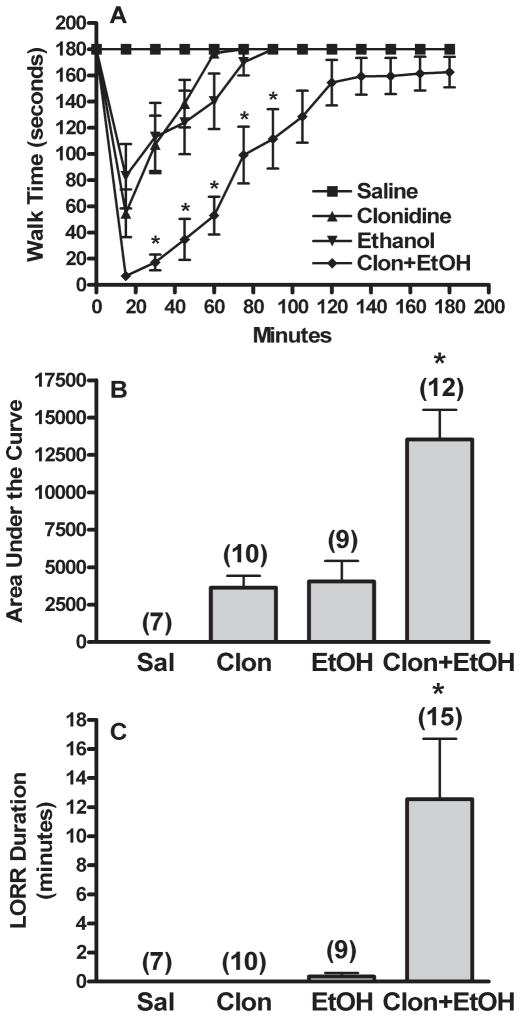
Fig. 1.
Clonidine synergistically enhances ethanol-evoked behavioral impairment. Rotorod time courses (A), corresponding area under the curve (AUC, B), and LORR durations (C) are shown for groups pretreated i.c. with aCSF prior to 2 i.v. injections of: (i) saline + saline (Sal or Saline), (ii) 60 μg/kg clonidine + saline (Clon or Clonidine), (iii) saline + 1 g/kg ethanol (EtOH or Ethanol), or (iv) 60 μg/kg clonidine + 1 g/kg ethanol (Clon + EtOH). The number of animals per group is shown in parentheses above the bar graphs. (Note: A few additional animals were tested for LORR only in the Clon + EtOH group.) p < 0.05, *differs from Sal, Clon, and EtOH (rotorod trends also differed from Clon + EtOH). Clon + EtOH AUC was significantly greater than the sum of the AUC for Clon and EtOH (synergistic interaction).