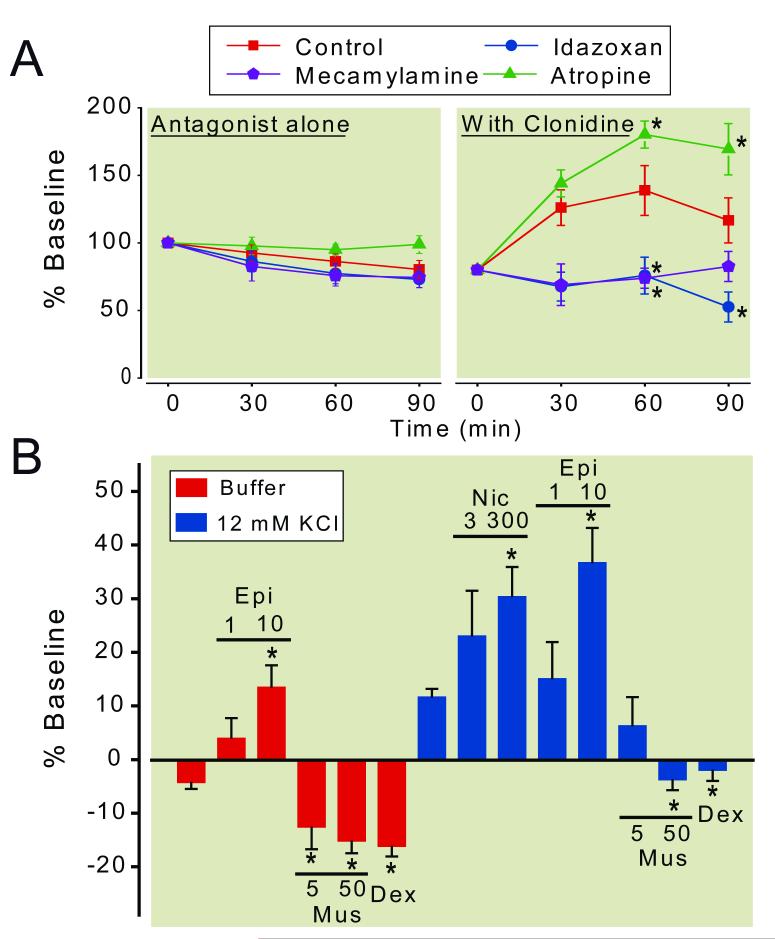
Figure 2.
(A) Effects of α2-adrenergic and cholinergic antagonists on clonidine-induced γ-amino butyric acid (GABA) release in the spinal dorsal horn ipsilateral to spinal nerve ligation (SNL). Buffer (control), idazoxan (300 μM), atropine (100 μM), or mecamylamine (100 μM) in the absence or presence of clonidine (100 μM) was perfused into the spinal dorsal horn through the microdialysis probe. Data are presented over time as percentage of baseline. N = 6-9. * p < 0.05 versus control. (B) Effects of α2-adrenergic and cholinergic agonists on GABA release in the synaptosomes from the spinal dorsal horn ipsilateral to SNL surgery. Synaptosomes were treated with epibatidine (Epi, 1-10 μM), nicotine (Nic, 30-300 μM), muscarine (Mus, 5-50 μM), or dexmedetomidine (Dex, 10 nM) in the presence or absence of 12 mM KCl. Data are presented as percentage of baseline. N = 6-10. * p < 0.05 versus buffer or KCl alone.