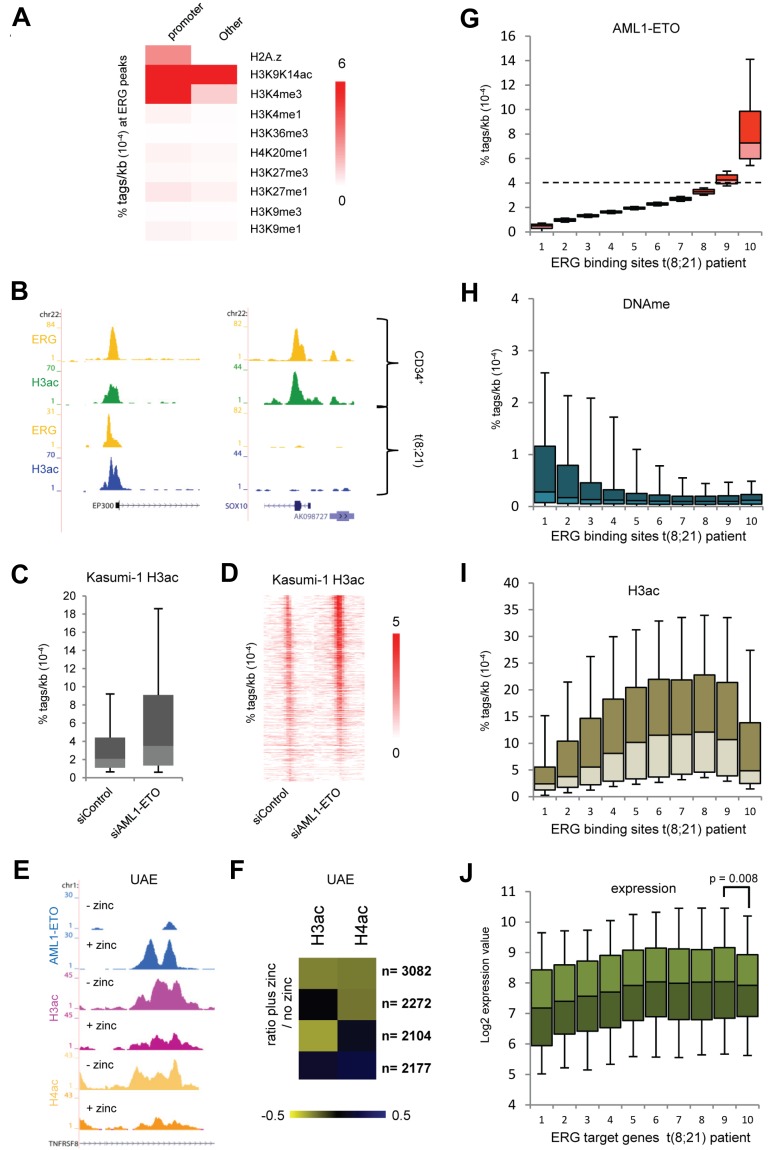
Figure 7.
ERG defines H3 acetylation signatures in normal CD34+ and t(8;21) blast cells. (A) Heatmap displaying median tag densities of a variety of chromatin modifications at ERG binding sites that are present in normal CD34+ cells. (B) Overview of the SOX10 and P300 genes in normal CD34+ and AML cells with t(8;21). Yellow represents the ERG ChIP-seq data; green, the H3K9K14ac using normal CD34+ cells; and blue, the H3K9K14ac data using patient AML CD34+ cells with t(8;21). (C-D) Boxplot (C) and intensity plot (D) showing the H3K9ac tag density at high-confidence AML1-ETO binding sites in control and AML1-ETO silenced Kasumi-1 cells. (E) ChIP-seq using U937 cells expressing (+ zinc) or not expressing (− zinc) AML1-ETO. Overview of the TNFRSF8 AML1-ETO binding site in U937 AML1-ETO cells. Blue represents the AE ChIP-seq data; purple, the H3ac data; and yellow, the H4ac data. (F) Heatmap displaying the log2 ratio of H3ac or H4ac tags at AML1-ETO target regions in zinc treated cells versus untreated cells. (G-I) Boxplots showing the density of AML1-ETO (G), MethylCap-DNAme (H), and H3ac (I) tags in patient AML t(8;21) cells within 10 bins of ERG binding sites (pz12) that are ranked according to AML1-ETO tag density. The dotted line in panel G separates the ERG sites not bound by AML1-ETO (bins 1-8) from those bound by AML1-ETO (bin 10). (J) Boxplot showing log2 expression values of the genes targeted by both AML1-ETO and ERG (predominantly bin 10) or ERG alone in 22 t(8;21) patients.