Figure 7.
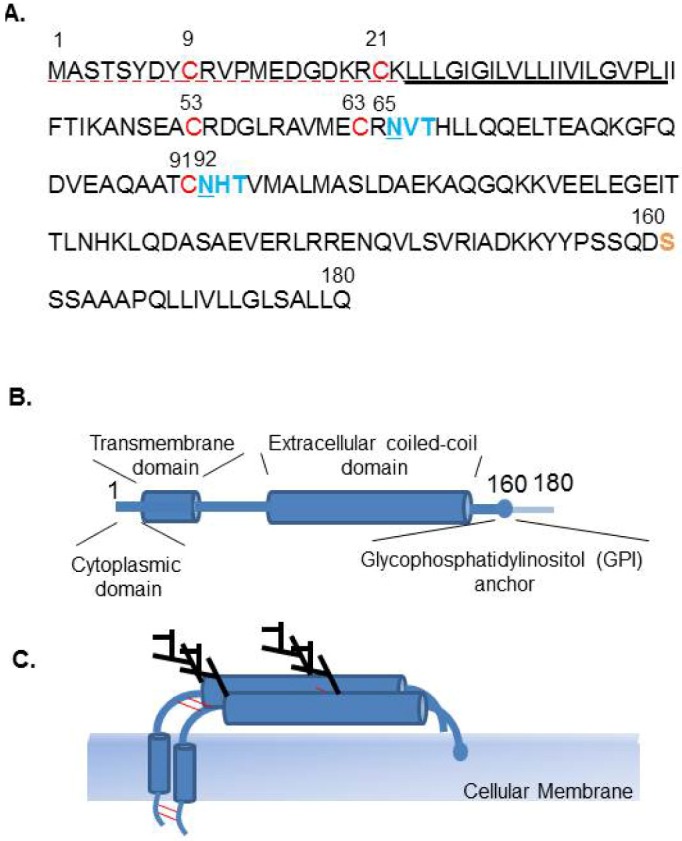
Characteristics of human Tetherin. (A) Amino acid sequence of human Tetherin (accession number NP_004326). Dashed red underline (1-22) indicates the cytoplasmic domain (CD), underline indicates the transmembrane domain (TM). Red font (C9, C21, C53, C63, and C91) indicates amino acids that may be responsible for disulfide bond formation and dimerization. Blue font indicates potential N-linked glycosylation motif (N‑X-S/T) and site (underlined). Serine (S) at position 160 is indicated as the site of cleavage prior to the C-terminal addition of a GPI anchor in yellow font. (B) Schematic representation of the domain structure of Tetherin, a type II transmembrane protein. (C) Tetherin forms a homodimer, through a C-C disulfide bond. Two sites of N‑glycosilation are also indicated.
