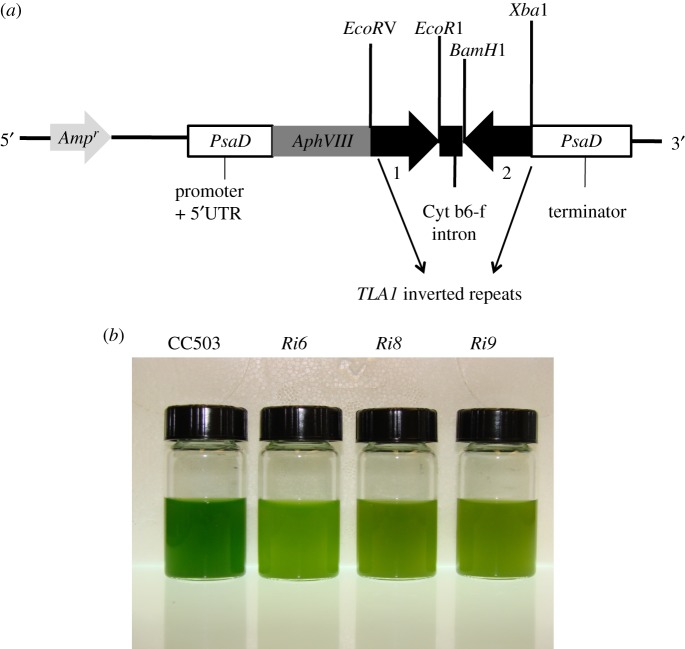
Figure 2.
(a,b) Downregulation of expression of TLA1 by RNA interference. (a) pSL72-TLA1 RNAi construct for downregulation of the TLA1 gene. The two reverse complementary inverted repeats (1 and 2) of the TLA1 gene sequence (thick black arrows) were cloned in the pSL72 vector under the control of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii PsaD promoter and terminator (white boxes). Upstream from the cloned inverted repeats of TLA1, the construct also contained the AphVIII (light grey arrow) and Ampr (dark grey arrow) genes, encoding paromomycin and ampicillin resistance, respectively. The AphVIII gene is also under the control of the PsaD promoter. The cleavage sites of restriction enzymes used for cloning of the two inverted repeats are shown. (b) Phenotype of three TLA1 RNAi transformants and parental wild-type strains of C. reinhardtii. Minimal media (TBP) liquid cultures of TLA1 RNAi transformants (Ri6, Ri8 and Ri9) and the wild-type CC503 are shown. Cell densities of the four cultures were approximately 8 × 106 cells ml−1. The putative TLA1 RNAi transformants (Ri6, Ri8 and Ri9) showed a lighter green coloration compared with the wild type, indicating a lower-level of chlorophyll content in these cells.