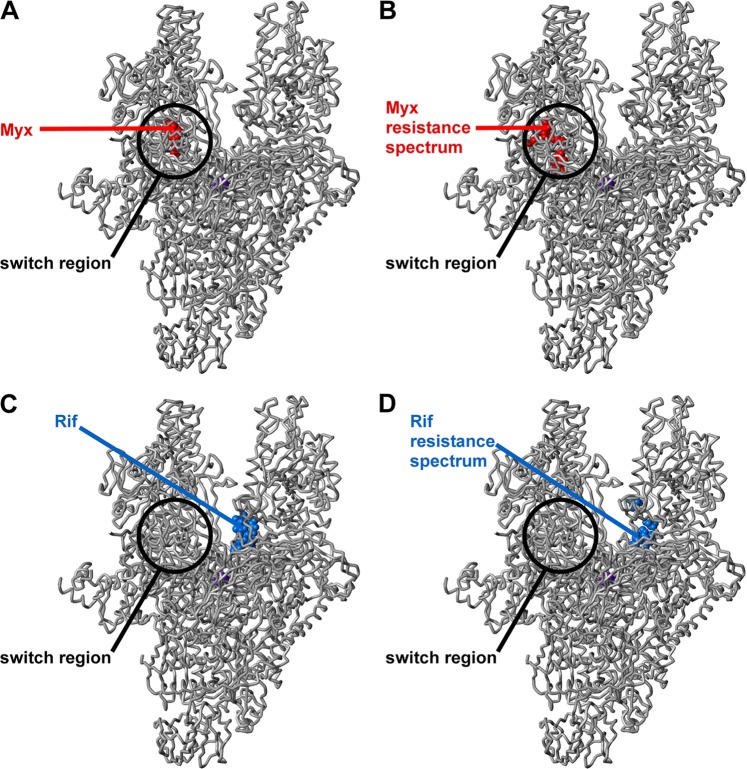
Fig 1.
Locations of binding sites and sites of resistance substitutions for Myx and Rif in the structure of bacterial RNAP. (A) Binding site for Myx (Myx shown in red) (32). (B) Resistance spectrum for Myx in S. aureus (sites of Myx-resistant substitutions identified in this study shown in red) (Table 3). (C) Binding site for Rif (Rif shown in blue) (6). (D) Resistance spectrum for Rif in S. aureus (sites of Rif-resistant substitutions identified in this study shown in blue) (Table 4). Atomic coordinates for RNAP and Myx are from a crystal structure of the Thermus thermophilus RNAP-Myx complex (32) (Protein Data Bank [PDB] accession code 3DXJ; σ subunit and β′ subunit nonconserved regions omitted for clarity). Atomic coordinates for Rif are from the crystal structure of the Thermus aquaticus RNAP-Rif complex (6) (PDB accession code 1I6V). The RNAP active-center Mg2+ is shown as a violet sphere for reference.