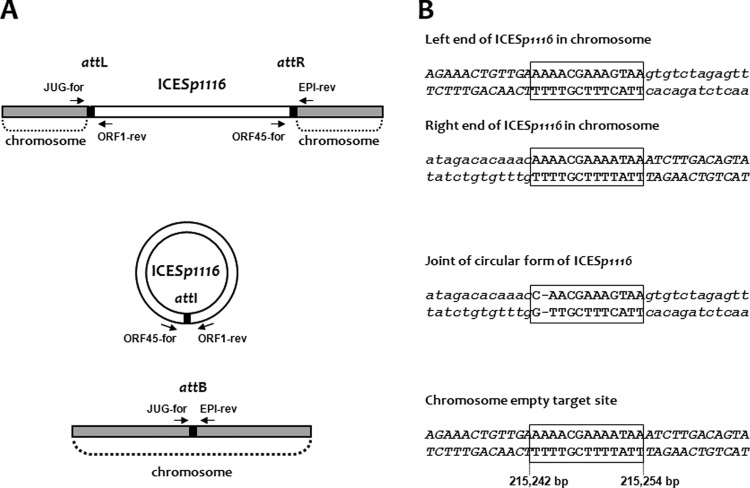
Fig 2.
Detection of excision of ICESp1116 from the genome. (A) Scheme of primer binding sites on the element and the genome. The chromosomal region is shown in gray, and ICESp1116 is in white. The integrated (top) and circular (center) forms of the element are shown, as is the regenerated target after excision (bottom). The core integration site is shown as a black box. Oligonucleotide primers and their direction of priming are represented by arrows. The primer pairs JUG-for/ORF1-rev and ORF45-for/EPI-rev detect the junctions between the genome and ICESp1116 (attL and attR, respectively), ORF45-for/ORF1-rev detects the circular form (containing attI) of ICESp1116, and JUG-for/EPI-rev detects the empty target site (containing attB). (B) Partial nucleotide sequences of the ICESp1116 integrated form at the left and right junctions (top), of the circular form (center), and of the chromosomal empty target site (bottom), showing the putative core sites (boxed sequences in uppercase roman letters), corresponding to bases 215,242 to 215,254 of the S. pyogenes Alab49 genome (accession no. CP003068). Nucleotides belonging to ICESp1116 are in lowercase italics; nucleotides belonging to the S. pyogenes A-3 chromosome are in uppercase italics.