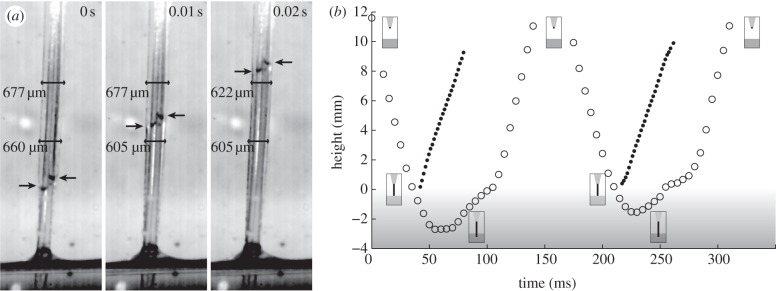
Figure 2.
Capillary suction through the hummingbird's tongue. (a) A dorsal view of the tongue of a hummingbird drinking sucrose solution of 20% concentration by mass. The arrows indicate the two menisci of the rising nectar. The tongue width becomes smaller after the inner surface is wetted by the nectar. (b) The position of the tongue tip (open circles) and meniscus (filled circles) during two consecutive licks. The measurement is interrupted when the meniscus moves beyond the field of view. The nectar rise speed is approximately 20 cm s−1 (see electronic supplementary material, movie S2). The capillary rise of the nectar clearly precedes the tongue retraction.