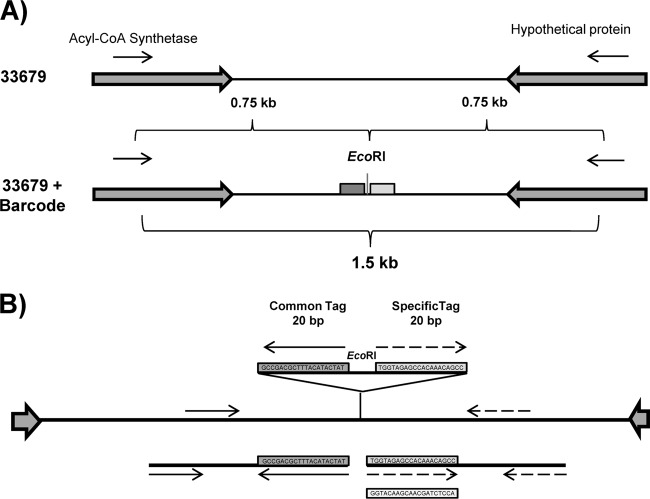
Fig 1.
Barcode module design. (A) Barcode modules are integrated into the chromosome between convergently transcribed genes or operons (long filled arrows) in intergenic regions larger than 500 bp. Primers (arrows) are designed to amplify an ∼1,500-bp flanking region surrounding the barcode to verify the insertion. (B) Barcode modules consist of two 20-nucleotide tags flanking an EcoRI restriction site. Real-time PCR assays are designed such that one of the tags serves as a primer binding site (arrows) to generate an amplicon using a second primer that anneals to a region of the chromosome flanking the barcode module. One of the tags (the common tag) is present in all barcoded strains, with a second tag (the specific tag) that serves as a unique identifier for each individual strain.