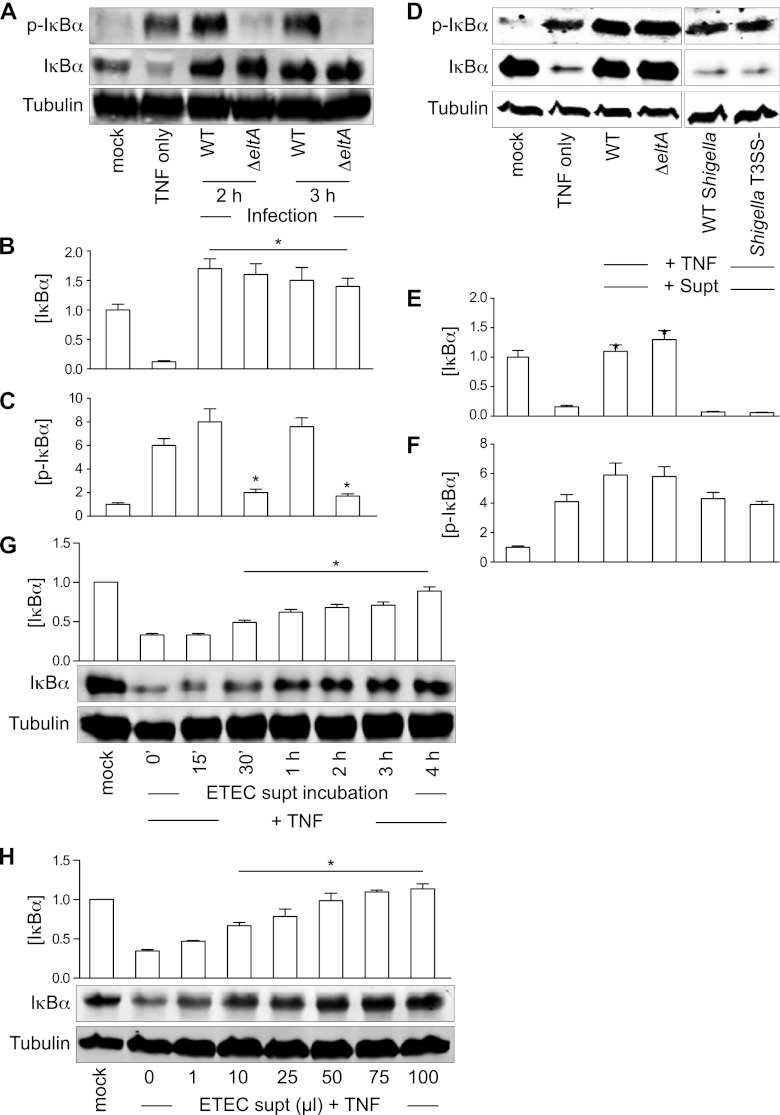
Fig 1.
ETEC supernatants protect IκBα from TNF-induced degradation. (A) Immunoblotting of total and phospho(Ser32/36)-IκBα after TNF stimulation or ETEC (WT or ΔeltA mutant) infection. Tubulin immunoblotting was used to normalize protein abundance for quantification. (B and C) Quantification of IκBα and phospho(Ser32/36)-IκBα abundance from data shown in panel A. Asterisks indicate protein abundance significantly different from that in the TNF-only lane. (D) Immunoblotting of total and phospho-IκBα after incubating HCT-8 cells with ETEC or Shigella supernatants (supt) and then stimulating the cells with TNF. (E and F) Quantification of IκBα and phospho(Ser32/36)-IκBα abundance from data shown in panel D. Asterisks indicate protein abundance significantly different from that in the TNF-only lane. (G) IκBα protection as a function of incubation time with the ETEC supernatant. Asterisks indicate protein abundance significantly different from that in the TNF-only lane. (H) IκBα protection as a function of ETEC supernatant volume. Asterisks indicate protein abundance significantly different from that in the TNF-only lane.