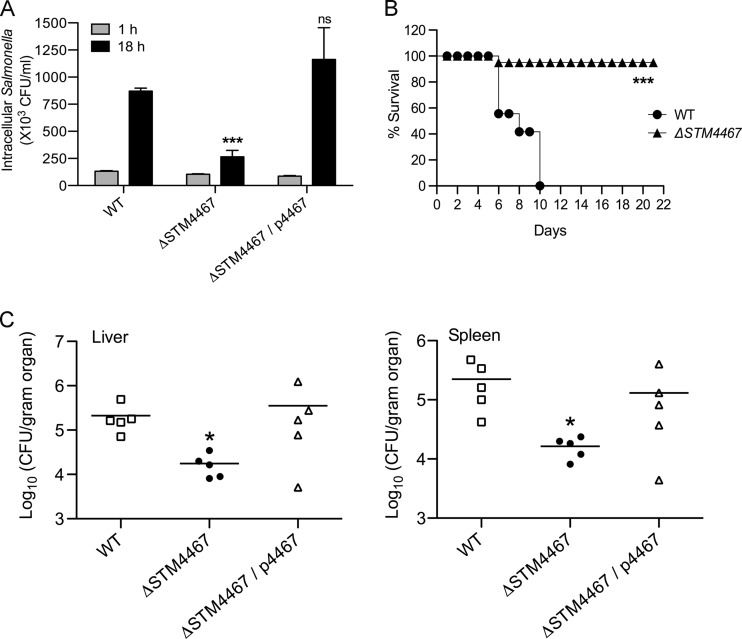
Fig 2.
The STM4467 gene contributes to S. Typhimurium virulence. (A) J774A.1 macrophage cells were infected with the wild-type (WT) strain (14028s), the STM4467 deletion mutant (CH102), or strain CH102 harboring the p4467 plasmid (ΔSTM4467/p4467). The numbers of intracellular bacteria were determined at 1 and 18 h after infection by using the gentamicin protection assay. Means and standard deviations from at least three independent experiments are shown. Triple asterisks indicate that the numbers of bacteria were significantly different (P < 0.001) from those of the WT strain at 18 h postinfection; ns, not significantly different. (B) Groups of C3H/HeN mice (5 mice/group) were injected intraperitoneally with ∼104 cells of the WT or STM4467 deletion strain. The survival of the mice was monitored daily for 3 weeks. The results of one of two independent experiments (P < 0.001), which yielded similar results, are shown. The results of the other experiment are shown in Fig. S1 in the supplemental material. (C) Groups of C3H/HeN mice (5 mice/group) were infected with the WT strain, the STM4467 deletion mutant, or strain CH102 harboring plasmid p4467 as described for panel B. At 5 days after infection, the numbers of bacteria in the liver and spleen were determined. An asterisk indicates that the numbers of bacteria were significantly different (P < 0.05) from those of the WT strain.