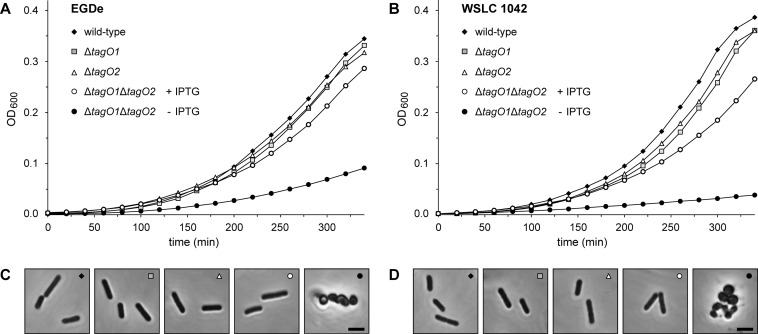
Fig 3.
Effect of tagO disruption on growth and cell morphology of L. monocytogenes. Growth response and changes in cell morphology were analyzed for parental, single ΔtagO1 and ΔtagO2 deletions, and conditional ΔtagO1 ΔtagO2 double-deletion mutants. All cells were cultured in BHI broth without antibiotics, and conditional ΔtagO1 ΔtagO2 double-deletion mutants were grown in the presence or absence of IPTG. Growth was monitored (as OD600) over the indicated time period. (A) L. monocytogenes serovar 1/2a wild-type strain EGDe and mutants EGDeΔtagO1, EGDeΔtagO2, and EGDeΔtagO1ΔtagO2::pLIV2(tagO1) with and without IPTG. (B) L. monocytogenes serovar 4b wild-type strain WSLC 1042 and mutants 1042ΔtagO1, 1042ΔtagO2, and 1042ΔtagO1ΔtagO2::pLIV2(tagO1) with and without IPTG. (C and D) Phase-contrast microscopy of cell samples taken from log-phase cultures of strain EGDe and derivatives (C) and strain WSLC 1042 and derivatives (D). In the double-deletion mutants, the drastic effect of complete tagO functional disruption on cell shape and morphology is clearly visible. Bars, 2 μm.