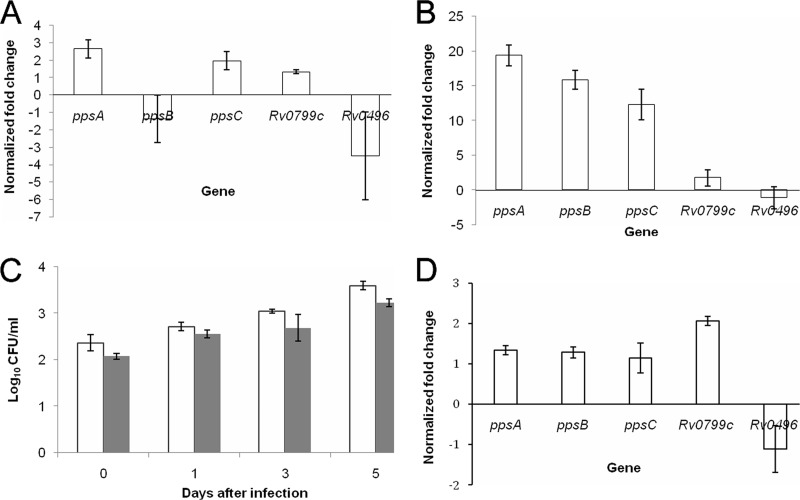
Fig 2.
Effects of rpoB S450L mutation on M. tuberculosis gene expression and fitness. (A) Expression of the PDIM biosynthesis locus in the rpoB mutant Beijing strain relative to the rifampin-sensitive wild-type parent strain during logarithmic growth in nutrient-rich broth, as measured by RT-PCR. (B) Gene expression of the same strains after 72 h of infection in activated murine macrophages. (C) Growth and survival of the rpoB mutant (gray) relative to the Beijing wild-type parent strain (white) in activated murine macrophages. (D) RT-PCR analysis of gene expression in a laboratory-generated RpoB S450L mutant relative to the isogenic CDC1551 wild-type strain during logarithmic growth in nutrient-rich broth. The CT obtained for each gene of interest was normalized with that of the housekeeping gene sigA. Fold regulation of individual genes was calculated using the following formula: 2−[C(CT) −S(CT)], where C represents the wild-type (control) strain and S represents the rpoB mutant strain. The error bars indicate standard deviations.