Figure 5. Voltage-dependent blockage of the of inward Na+ current by intracellular organic cations in WT and T360A mutant channels.
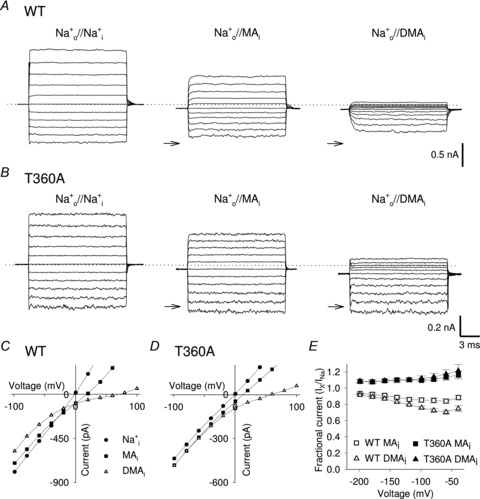
A, representative macroscopic WT current recordings from one excised patch in Na+ symmetrical conditions and when intracellular Na+ was replaced by an equimolar amount of MA and DMA. Currents were elicited in the presence of 1 mm cGMP in the bathing medium and voltage steps ranging from −100 to +100 mV (ΔV = 20 mV). Dashed line indicates 0 current level; arrows indicate the −100 mV Na+ current level in symmetrical solution. B, as in A, but for T360A mutant channel. C, I–V curves in WT channels in the presence of 110 mm intracellular Na+ (filled circles), MA (filled squares) and DMA (open triangles). D, as in C, but for T360A mutant channel. E, dependency of IX/INa on voltage when MA ions (open and filled squares) and DMA ions (open and filled triangles) were in the bathing medium for WT (open symbols; n≥ 5), and T360A (filled symbols; n = 4) mutant channel, respectively.
