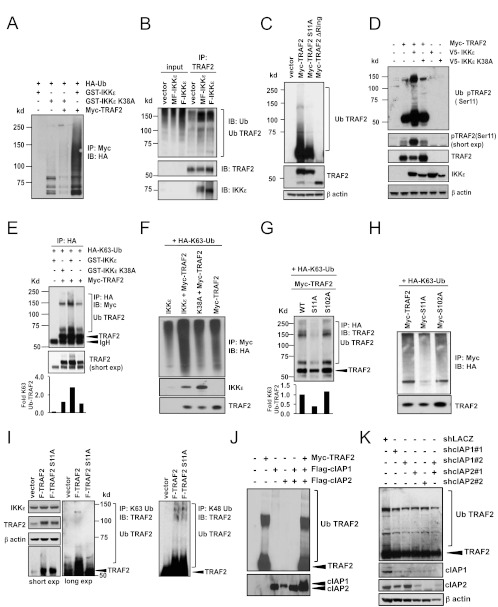
Fig 5.
IKKε promotes TRAF2 Lys63-linked ubiquitination. (A) Total TRAF2 ubiquitination in HEK293T cells cotransfected as indicated with HA-Ub. Myc-TRAF2 immune complexes were isolated and analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with an HA antibody. (B) Endogenous TRAF2 ubiquitination in HMLEM cells expressing a control vector, MF-IKKε, and F-IKKε. TRAF2 immune complexes were isolated and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies specific for ubiquitin, TRAF2, or IKKε. (C) Wild-type TRAF2 and TRAF2 S11A ubiquitination. HEK293T cells were transfected as indicated and analyzed by immunoblotting with a TRAF2 antibody. (D) Ubiquitination of phosphorylated TRAF2 in the presence of IKKε. HEK293T cells were cotransfected as indicated and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies specific for phospho-TRAF2 (Ser11) [pTRAF2 (Ser11)], TRAF2, IKKε, or β-actin. The short exposure (exp) shows pTRAF2 (Ser11). (Top) Ubiquitinated pTRAF2 (Ser11). (E and F) Lys63-linked TRAF2 ubiquitination in the presence of IKKε. HEK293T cells were cotransfected as indicated with HA-K63-Ub. (E) Immunoprecipitation was performed using an HA antibody followed by immunoblot analysis of Myc-TRAF2. The short exposure shows Myc-TRAF2 above IgH. (F) Myc-TRAF2 immune complexes were isolated and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies specific for HA, IKKε, andTRAF2. (G and H) Lys63-linked ubiquitination of wild-type TRAF2 and TRAF2 phosphorylation mutants. HEK293T cells were cotransfected as indicated with HA-K63-Ub. (G) HA-K63-Ub immune complexes were isolated and analyzed by immunoblotting with a TRAF2 antibody. (H) Myc immune complexes were isolated and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies specific for HA and TRAF2. (I) K63- and K48-linked ubiquitination of TRAF2 in IKKε-dependent cells. MCF-7 cells were transduced with F-TRAF2 or F-TRAF2 S11A (expression levels are shown in the three upper left panels). Immune complexes isolated with a K63-linked polyubiquitin-specific (left) or K48-linked polyubiquitin-specific (right) antibody were analyzed for the presence of modified TRAF2. K48-linked polyubiquitin immunoprecipitations were performed following treatment with the proteasome inhibitor MG-132 (10 μm) for 4 h. (J) In vitro TRAF2 ubiquitination in the presence and absence of cIAP1 and cIAP2. Lys63-ubiquitination assay using immunoprecipitated Myc-TRAF2, Flag-cIAP1, and Flag-cIAP2, as indicated. All reactions were performed in the presence of recombinant E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme Ubc13 and ubiquitin and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (K) TRAF2 ubiquitination following cIAP1 and cIAP2 suppression. Ubiquitination of TRAF2 in MCF-7 cells expressing cIAP1-specific shRNA (shcIAP1#1 and shcIAP1#2) or cIAP1/cIAP2 dual-specific shRNA (shcIAP2#1 and shcIAP2#2) was analyzed by immunoblotting. Despite their nomenclature, the shcIAP2#1 and shcIAP2#2 target sequences are present in both cIAP1 and cIAP2.