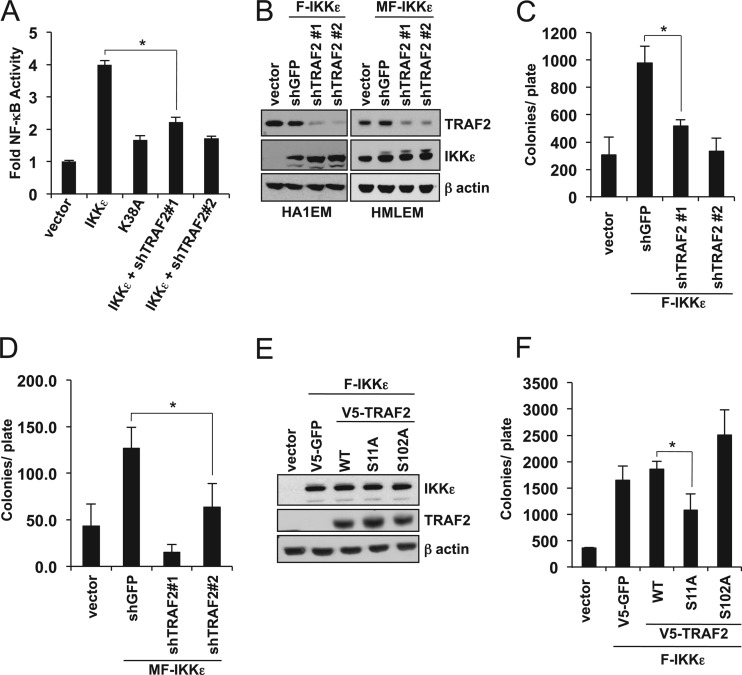
Fig 6.
TRAF2 is required for IKKε-induced NF-κB activation and transformation. (A) IKKε-induced NF-κB activity following suppression of TRAF2. HEK293T cells were cotransfected as indicated with SV40-Renilla luciferase and a NF-κB luciferase reporter. Raw light unit (RLU) activity was normalized to the activity observed with control vector. *, P = 5.2 × 10−5, calculated by a standard t test. (B) TRAF2 suppression in IKKε-transformed HA1EM and HMLEM cells. TRAF2 and IKKε immunoblots in control (vector), HA1EM-F-IKKε, and HMLEM-MF-IKKε cells following transduction with shTRAF2#1, shTRAF2#2, or control shGFP. β-Actin was analyzed as a loading control. (C) Anchorage-independent growth of IKKε-transformed HA1EM cells following TRAF2 suppression. Colony formation of HA1EM cells used in the experiment whose results are shown in panel B was analyzed after 28 days. *, P = 4.7 × 10−5, calculated by a standard t test. (D) Anchorage-independent growth of IKKε-transformed mammary cells following TRAF2 suppression. Colony formation of HMLEM cells used in the experiment whose results are shown in panel B was analyzed after 28 days. *, P = 0.0011, calculated by a standard t test. (E) TRAF2 overexpression in IKKε-transformed HA1EM cells. Immunoblot of TRAF2 and IKKε in control (vector) HA1EM or HA1EM-F-IKKε cells transduced with V5-GFP, V5-TRAF2, V5-TRAF2 S11A, or V5-TRAF2 S102A. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (F) Anchorage-independent growth of IKKε-transformed cells in the presence of TRAF2. Colony formation of cells used in the experiment whose results are shown in panel E was assayed after 28 days. *, P = 0.0045, calculated by a standard t test. The mean ± SD of three experiments is shown for all panels.