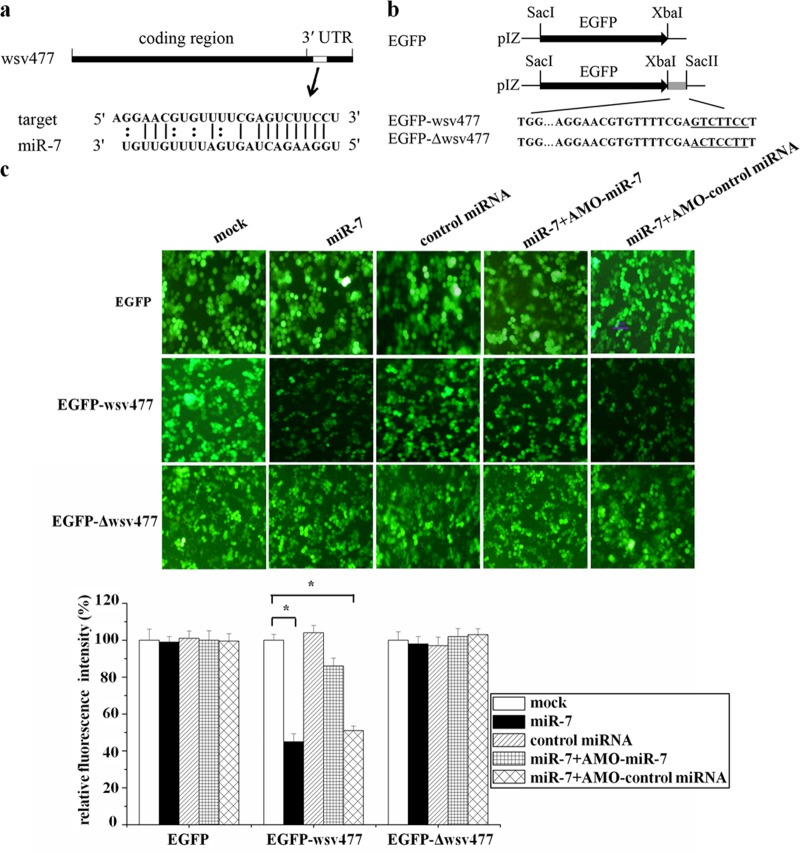
Fig 1.
Interaction between host miR-7 and viral wsv477 gene. (a) The region of the wsv477 3′UTR sequence targeted by miR-7 predicted with TargetScan. The seed sequence of miR-7 is underlined. (b) Constructs of the wild-type and mutated 3′UTRs of the viral wsv477 gene. The sequences complementary to the seed region of miR-7 are underlined. (c) Interaction between host miR-7 and the viral wsv477 gene in insect cells. The insect High Five cells were cotransfected with miR-7 and different plasmids (EGFP, EGFP-wsv477, or EGFP-Δwsv477). To act as a control, the control miRNA was included in the transfections. The constructs EGFP-wsv477 and EGFP-Δwsv477 contained the wild-type and mutant wsv477, respectively. To inhibit the activity of miR-7, the plasmid (EGFP, EGFP-wsv477, or EGFP-Δwsv477)-transfected cells were transfected simultaneously with miR-7, AMO-miR-7, or AMO-control miRNA. At 48 h after transfections, fluorescent images were obtained (upper panel). Lane headings indicate the miRNAs and LNA-modified anti-miRNA oligonucleotides (AMOs) that were used. The plasmids that were used for transfections are indicated on the left. The effects of the miRNAs and/or AMOs on gene expressions of the different plasmids (EGFP, EGFP-wsv477, or EGFP-Δwsv477) were determined by comparing fluorescence intensities in the absence of miRNAs and/or AMOs with that of the mock transfection (lower panel). *, statistically significant differences (P < 0.05).