Fig 6.
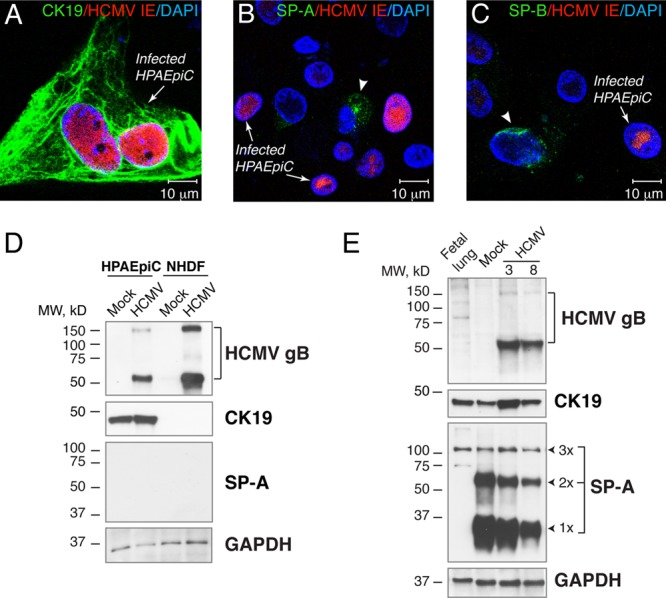
HCMV productively infects primary human pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells (HPAEpiC) and lung implants. (A to C) HPAEpiC were maintained in vitro for 5 days, inoculated with VR1814 at an MOI of 1, and fixed and costained for HCMV IE and CK19 (A), SP-A (B), and SP-B (C) 4 days after inoculation. The arrows show infected cells, and the arrowheads show cells expressing SP-A (B) or SP-B (C). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. (D and E) Western blot analysis of HCMV gB, CK19, and SP-A in HPAEpiC inoculated with VR1814 at an MOI of 1 and NHDF inoculated at an MOI of 0.1 (D) or lung implants (cohort F) inoculated with HCMV at 5.8 log10 IU/implant (E). Total proteins from 10 μg for cells and 50 μg for implants or preimplantation lungs (20 weeks) were subjected to 12% SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions and subsequently electroblotted. The expression level of GAPDH was used as a loading control. The results are representative of those observed for 16 infected and mock-infected implants obtained from two different lungs (cohorts A and F) (E). 1×, SP-A monomer (28 to 36 kDa); 2×, SP-A dimer (64 kDa), 3×, SP-A oligomer (>100 kDa); fetal lung, preimplantation lung (20 g.w.); 3 and 8, mouse 3 and mouse 8.
