Abstract
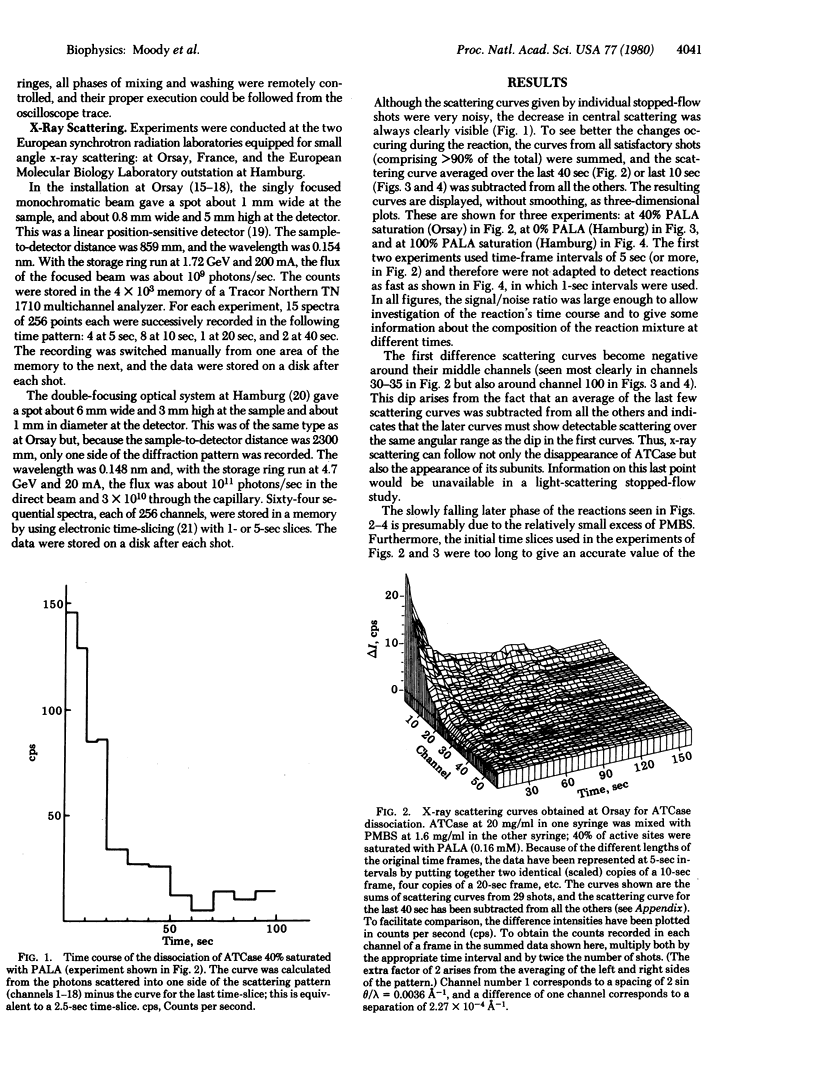
A combination of stopped-flow and x-ray scattering techniques was used to study the dissociation of aspartate transcarbamylase (carbamoylphosphate:L-aspartate carbamoyltransferase, EC 2.1.3.2) with a 2:1 excess of p-chloromercuribenzenesulfonic acid (the ratio being calculated on a basis of reactive sites), in the presence and absence of the transition state analogue N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate. At 10 mg of protein per ml, the scattering curves allowed some details of the reaction to be followed with a time resolution down to 1 sec. The curves showed not only the dissociation of the enzyme complex but also the formation of the subunits. These results show that, with present facilities, x-ray scattering could be used to study dissociation or reassociation reactions with a time resolution of the order of 100 msec.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackburn M. N., Schachman H. K. Allosteric regulation of aspartate transcarbamoylase. Effect of active site ligands on the reactivity of sulfhydryl groups of the regulatory subunits. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):5084–5091. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin S. B., Cannell D. S. The effect of succinate on the translational diffusion coefficient of aspartate transcarbamylase. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):192–195. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. R., McMurray C. H., Lipscomb W. N. The thiol group in the catalytic chains of aspartate transcarbamoylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3638–3642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. R., Pastra-Landis S. C., Lipscomb W. N. An intermediate complex in the dissociation of aspartate transcarbamylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1351–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J. C., Schachman H. K. Allosteric interactions in aspartate transcarbamylase. II. Evidence for different conformational states of the protein in the presence and absence of specific ligands. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):538–552. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J. C., Schachman H. K. Allosteric interactions in aspartate transcarbamylase. II. Evidence for different conformational states of the protein in the presence and absence of specific ligands. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):538–552. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J. C., Schachman H. K. Distinct subunits for the regulation and catalytic activity of aspartate transcarbamylase. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1054–1062. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson Q. H., Milnes L. Apparatus for rapid and sensitive spectrophotometry. Biochem J. 1964 Apr;91(1):161–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0910161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett G. J., Schachman H. K. Allosteric regulation of aspartate transcarbamoylase. Changes in the sedimentation coefficient promoted by the bisubstrate analogue N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):5077–5083. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner M. W., Schachman H. K. Conformational changes in proteins as measured by difference sedimentation studies. I. A technique for measuring small changes in sedimentation coefficient. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1900–1919. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner M. W., Schachman H. K. Conformational changes in proteins as measured by difference sedimentation studies. II. Effect of stereospecific ligands on the catalytic subunit of aspartate transcarbamylase. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1919–1926. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzati V., Tardieu A. Recent developments in solution x-ray scattering. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1980;9:1–29. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.09.060180.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody M. F., Vachette P., Foote A. M. Changes in the x-ray solution scattering of aspartate transcarbamylase following the allosteric transition. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 9;133(4):517–532. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilz I., Glatter O., Kratky O. Small-angle X-ray scattering. Methods Enzymol. 1979;61:148–249. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)61013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


