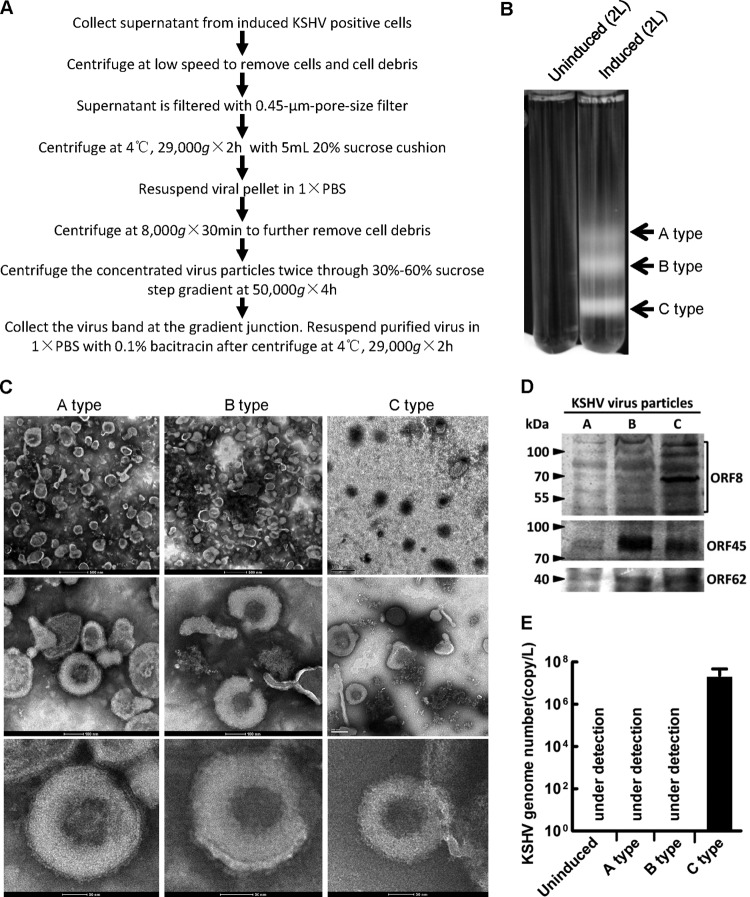
Fig 1.
Purification and verification of KSHV particles. (A) Procedures for purifying KSHV particles from induced supernatant of KSHV-positive cell lines. (B) Two liters of supernatant of uninduced BCBL-1 cells or induced BCBL-1 cells was loaded onto a 30 to 60% nonlinear sucrose gradient after condensation by ultracentrifugation. Three bands, indicated by arrows from top to the bottom, represent empty (A type), intermediate (B type), and mature KSHV particles, respectively. (C) KSHV particles negatively stained with tungstophosphoric acid were observed under an electron microscope. A scale bar is shown at the bottom or left corner of each image. (D) Immunoblot analysis with virus from the indicated bands from panel B for KSHV virion component ORF8 (glycoprotein B), ORF45 (tegument protein), and ORF62 (small capsid protein), respectively. (E) Quantification of viral genome copy using supernatant of uninduced or induced BCBL-1 cells by qPCR. Under detection indicates that the number of viral genomes is less than the detection limit of the primers, which is about 100 copies. The detailed protocol is stated in Materials and Methods. Data shown are the means ± standard deviations (SD) from three independent experiments.