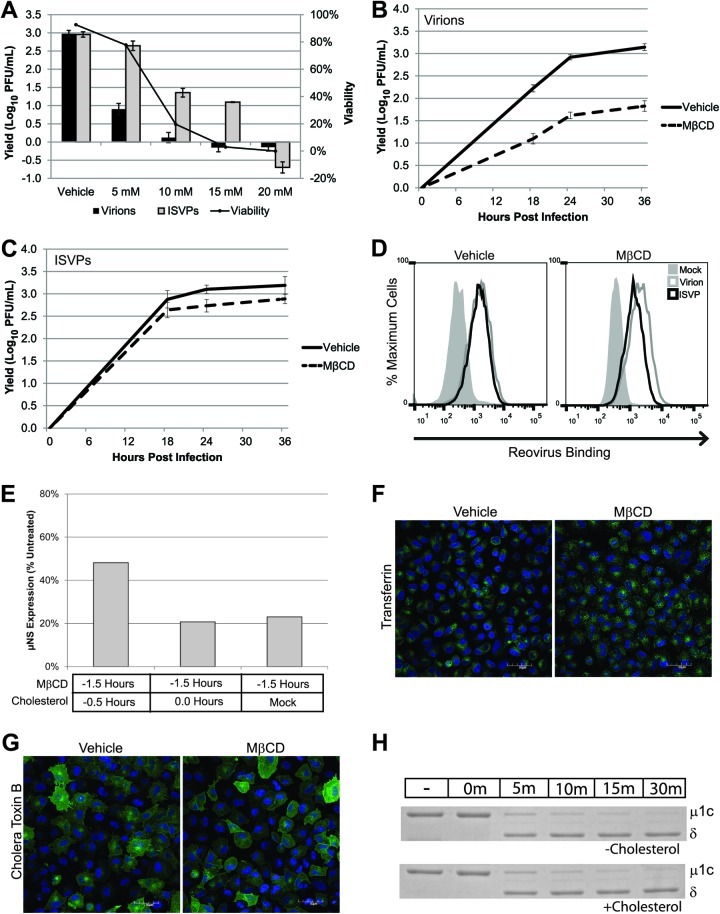
Fig 6.
Cholesterol plays a role in infection by reovirus virions. (A) L929 cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of MβCD, and viability was assessed at 24 hpi. A parallel set of samples was infected with T1L virions or ISVPs at an MOI of 3 and assayed for viral yield at 24 hpi. (B and C) L929 cells were pretreated with vehicle (water) or 5 mM MβCD and infected with reovirus T1L virions (B) or ISVPs (C) at an MOI of 3. Viral yields were determined at the indicated times postinfection by plaque assay on L929 cells. (D) L929 cells in suspension culture were pretreated with vehicle (water) or MβCD and adsorbed with reovirus virions (gray lines) or ISVPs (black lines) at a concentration of 1 × 105 particles/cell or an equivalent volume of gel saline (shaded peaks). After adsorption, cells were fixed and stained with an anti-reovirus T1L antibody. Reovirus binding was quantified by flow cytometry. (E) Cells were treated with MβCD for 1 h, and 0.1 mM water-soluble cholesterol was added prior to or at the time of adsorption. Infection was analyzed by immunoblotting for μNS at 24 hpi. (F and G) A549 cells were pretreated with vehicle (water) or MβCD for 1 h. Treated cells were incubated with prelabeled transferrin (F) or CTB (G). Warm medium was added to the cultures, and after 15 min cells were fixed and ligand uptake was visualized by confocal microscopy. Scale bars represent 50 μM. (H) Reovirus virions (5 × 1010) were incubated with chymotrypsin, cholesterol, or both in virion dialysis buffer at 32°C. At the indicated times, digestions were terminated with PMSF and the particles were visualized by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining.