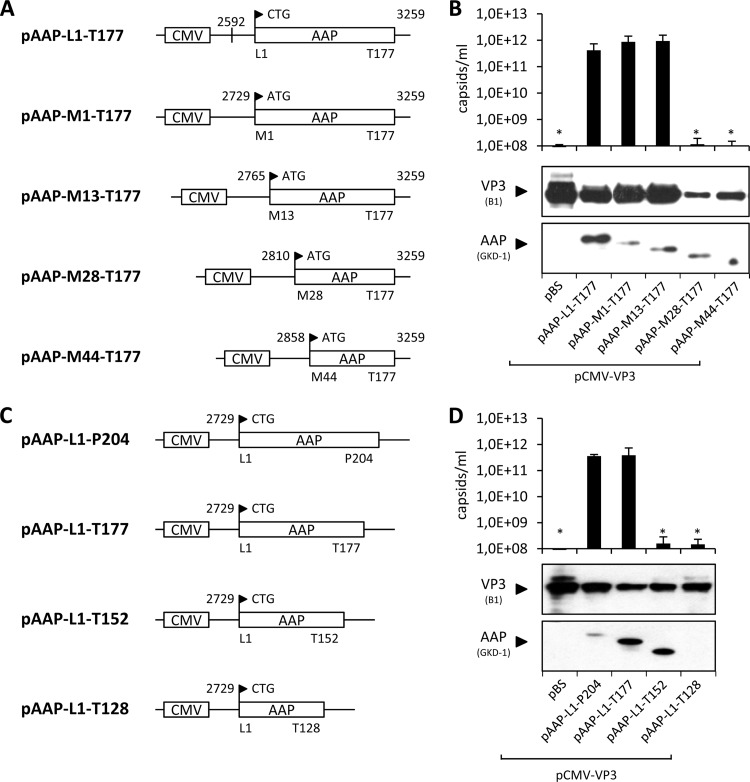
Fig 2.
Assembly-promoting activities of deletion mutant AAPs. N-terminal (A) and C-terminal (C) deletion mutant constructs of AAP were generated by site-directed mutagenesis. pAAP-L1-T177 was used as a control for the expression of AAP comprising the authentic, nonconventional translation initiation codon CTG. All N-terminal deletion constructs started with an ATG codon instead. The respective N- and C-terminal amino acids of each AAP construct are indicated together with their positions, as well as the respective nucleotide positions. (B and D) Capsid assembly was analyzed by cotransfection of 293T cells with pCMV-VP3 and the respective AAP expression plasmids and analyzed by A20 antibody-based capsid ELISA at 48 h posttransfection. Transfection of pCMV-VP3 together with an empty vector (pBS) served as a negative control. Protein expression was analyzed by Western blot assay using MAb B1 (detection of VP3) and the polyclonal anti-AAP serum GKD-1. Bars represent the average capsid titers of at least three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate capsid titers significantly lower than that obtained with pAAP-L1-T177 (P < 0.01).