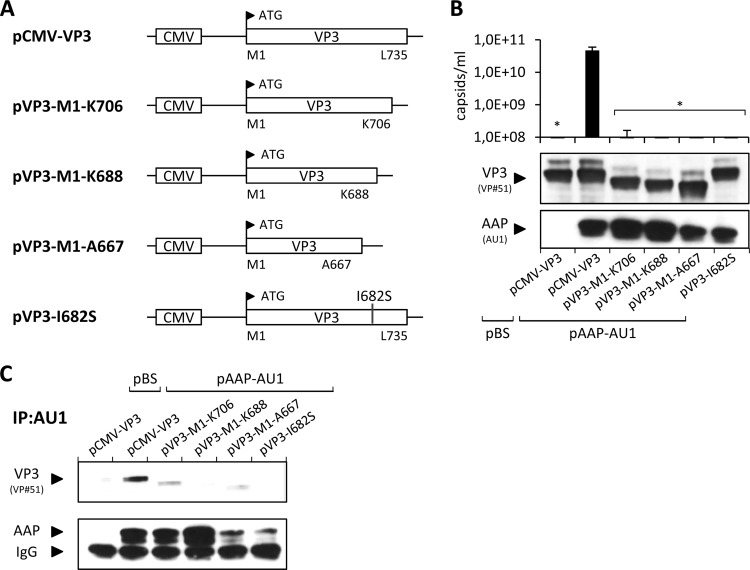
Fig 6.
Capsid assembly by VP deletion mutant constructs. (A) C-terminal deletions of VP3 and an I682S point mutation were generated by site-directed mutagenesis. pCMV-VP3 was used as a control for the expression of full-length VP3. The respective N- and C-terminal amino acids of each VP3 construct are indicated together with their positions. (B) Capsid assembly was analyzed by A20 antibody-based capsid ELISA of freeze-thaw lysates of 293T cells transfected with pAAP-AU1 and the respective mutant VP3 proteins. Coexpression of the empty pBluescript vector (pBS) served as a negative control. Protein expression was confirmed by Western blot analysis using VP#51 polyclonal serum (detection of VP) and anti-AU1 MAb (detection of AAP-AU1 tag). Bars represent the average capsid titers of at least three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate capsid titers significantly lower than that obtained with pCMV-VP3 (P < 0.01). (C) Immunoprecipitation (IP) of AAP-VP complexes from lysates of transfected 293T cells using anti-AU1 antibody-coupled protein A Sepharose. AAP and coprecipitated VP3 were detected by Western blot analysis using the anti-AU1 MAb and VP#51 polyclonal serum, respectively.