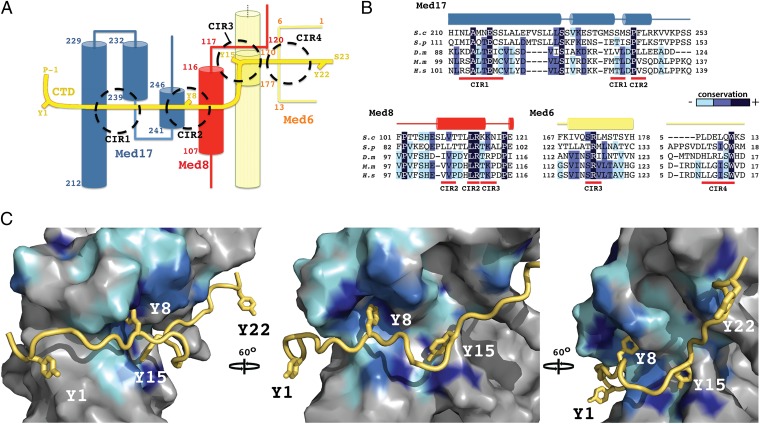
Fig. 3.
CTD-interacting regions of Mediator Head module. (A) Schematic representation of the path of the CTD (yellow) across the Head module. CTD tyrosines (Y1–Y22) and terminal residues are highlighted, as well as major interacting regions (CIR1-4; dashed circles). Secondary structure elements of the interacting Mediator polypeptides, Med17 (blue), Med8 (red), and Med6 (straw) are shown with corresponding residue numbering. (B) Sequence alignments covering the CTD-interacting regions of Med17, Med8, and Med6 from S cerevisiae (S.c), Shizosaccharomyces pombe (S.p), Drosophila melanogaster (D.m), Mus Musculus (M.m) and Homo sapiens (H.s). Conserved residues are shaded in dark blue, marine, and cyan, in order of decreasing conservation. Secondary structure elements are shown above the sequence. (C) Three views of a surface representation of the CTD (yellow)–Head module (gray) interaction, related by 60° rotations. Mediator sequence conservation in represented with surface coloring according to B. The CTD backbone is shown as a ribbon with the four tyrosines depicted as sticks.