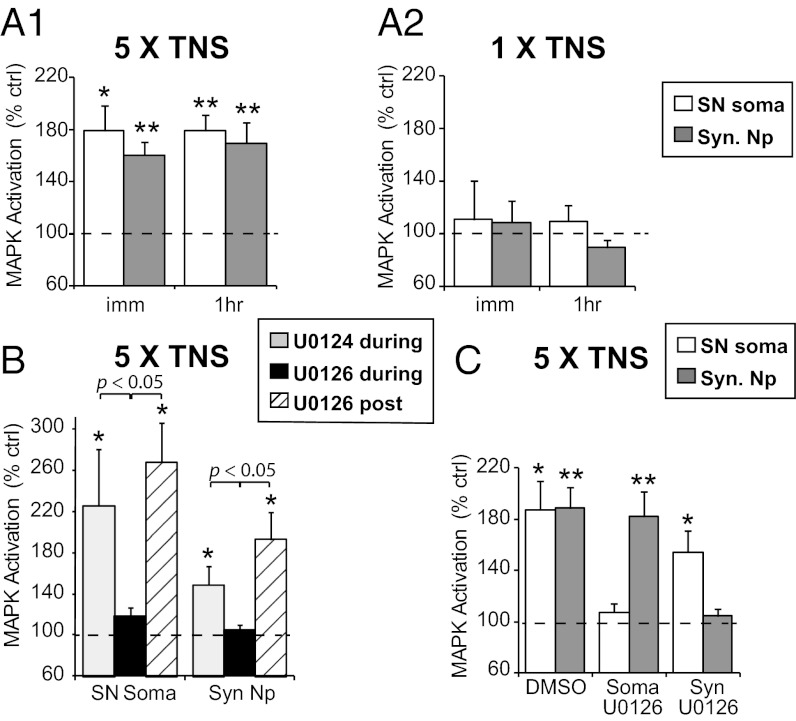
Fig. 1.
Spatiotemporal profiles of MAPK activation by TNS. (A1) MAPK activation is observed immediately (imm) and at 1 h (1hr) after repeated TNS in both SN soma and synaptic neuropil (Syn. Np). (A2) A single TNS does not give rise to immediate or 1-h MAPK activation in either compartment. (B) The presence of U0126 during, but not after, repeated TNS blocks 1-h MAPK activation, suggesting that persistent MEK activation is not required for sustained MAPK activation by TNS. (C) Somatic U0126 significantly blocks MAPK activation in SN soma without affecting MAPK activation in synaptic neuropil, and vice versa, suggesting independent activation of somatic and synaptic MAPK.