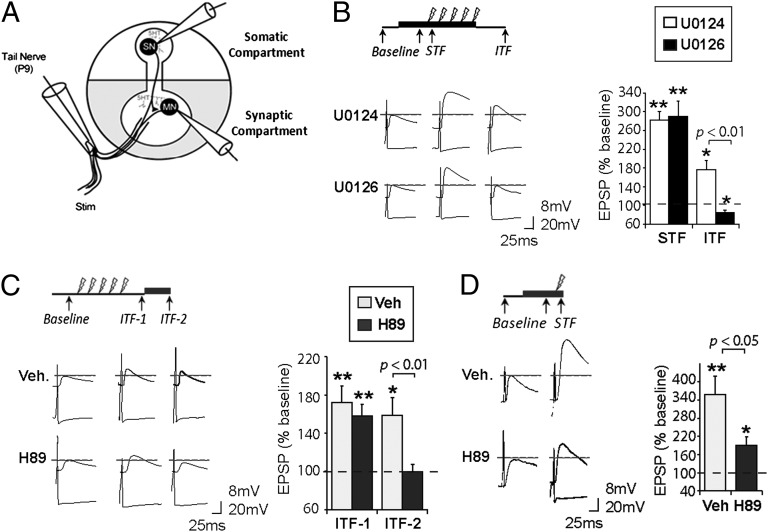
Fig. 4.
Requirement of synaptic MAPK and PKA activation for synaptic facilitation. (A) A diagram depicting intracellular recording from paired SNs and MNs in a two-chamber dish with application of inhibitors (shaded region) restricted to the synaptic compartment. (B) U0126 in the synaptic compartment during repeated TNS blocks ITF induction, without affecting STF. (C) H89 in the synaptic compartment after repeated TNS blocks ITF maintenance. (D) Blocking synaptic PKA activation by H89 significantly attenuats STF induced by a single TNS. Representative traces of synaptic facilitation are shown for each experiment. Data are presented as mean percent ± SEM of baseline EPSP.