Fig. 3.
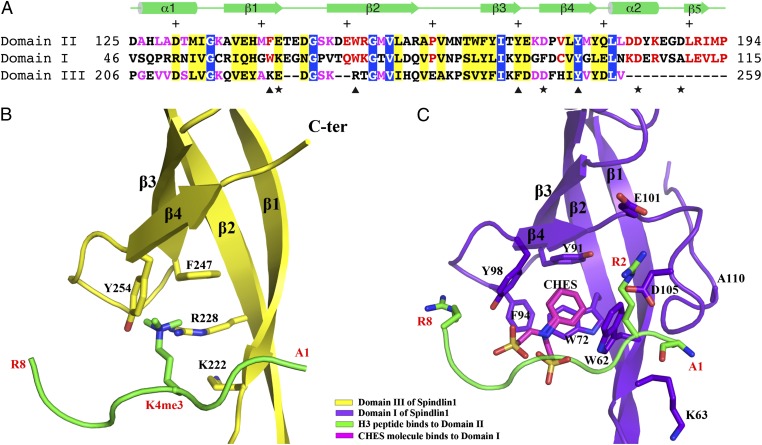
The first and third tudor-like domains of Spindlin1 are incapable of binding H3K4me3 peptide. (A) Sequence alignment of the three tudor-like domains. The positions of aromatic residues forming the H3K4me3-binding aromatic cage of domain II are indicated with triangles at the bottom of the sequences. The positions of four dicarboxylic amino acids that interact with the terminal amino group, H3R2, and H3R8 are indicated with stars. Identical and similar residues among all three domains are shown in white letters over blue background and black letters over yellow background, respectively. Identical and similar residues between domains II and I are shown in red letters, and those between domains II and III are shown in magenta. Secondary structural elements of domain II are shown above the sequence, and every 10 even residues are indicated with +. (B) Domain III of Spindlin1 shown in the same orientation as that of domain II in Fig. 2. The H3K4me3 peptide bound to domain II is superimposed to indicate that such a peptide cannot bind domain III due to lack of an intact aromatic cage. (C) Domain I of Spindlin1 shown in the same orientation as that of domain II in Fig. 2. The H3K4me3 peptide bound to domains II is superimposed to show that domain I lacks appropriate dicarboxylic amino acids and α2 required for H3K4me3 binding.