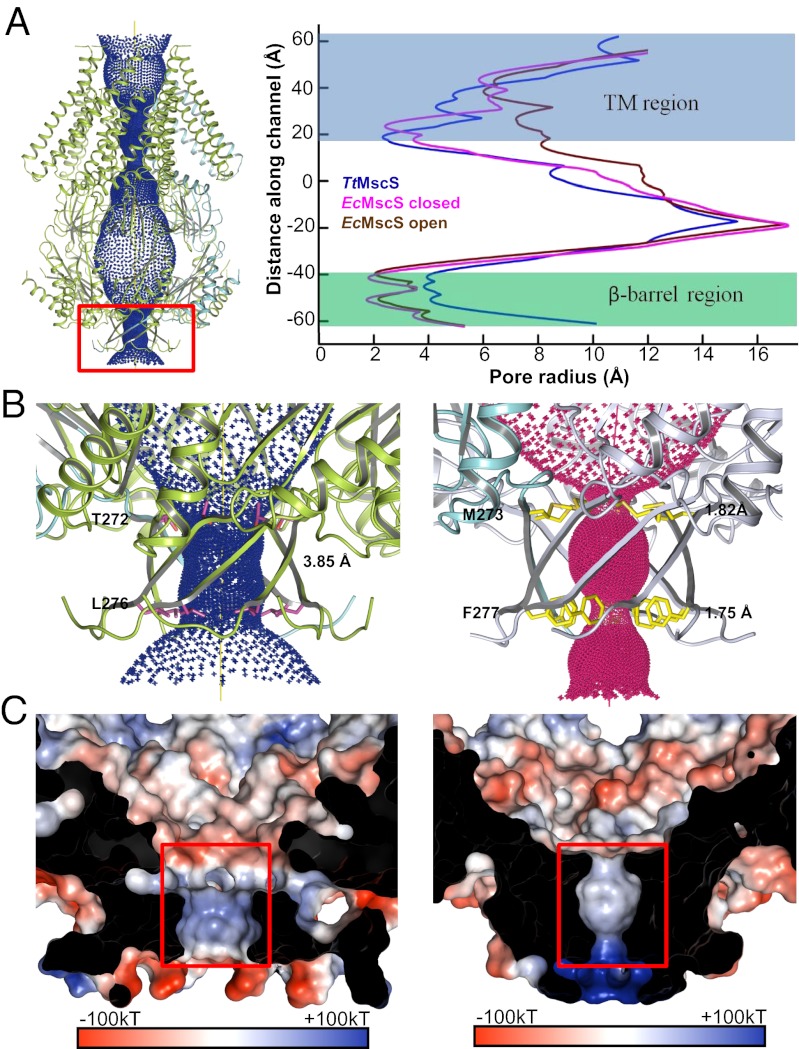
Fig. 4.
β-Barrel pore of TtMscS differs from that of EcMscS in size and electrostatic potential. (A) The central channel in TtMscS contains two constriction sites. The channel passage (Left), calculated by HOLE (26), is indicated by blue dots along a central yellow line. The radius of the channel is plotted on the right panel and compared with those from the closed and open states of EcMscS. The β-barrel region is highlighted by a red box. (B) The β-barrel pore of TtMscS is larger than that of EcMscS. The TtMscS and EcMscS β-barrel regions are shown at Left and Right, respectively. The two residues lining the restriction sites are shown as sticks and are labeled. The radii of the β-barrel pore of both channels are indicated. (C) The β-barrel pore of TtMscS has an electrostatic surface that is distinct from that of EcMscS. Left and Right: Electrostatic potentials around the β-barrel pore inner surface of TtMscS and EcMscS, respectively. The front of the β-barrel pore is cut away to reveal the inner surface. The orientation is the same as in B.