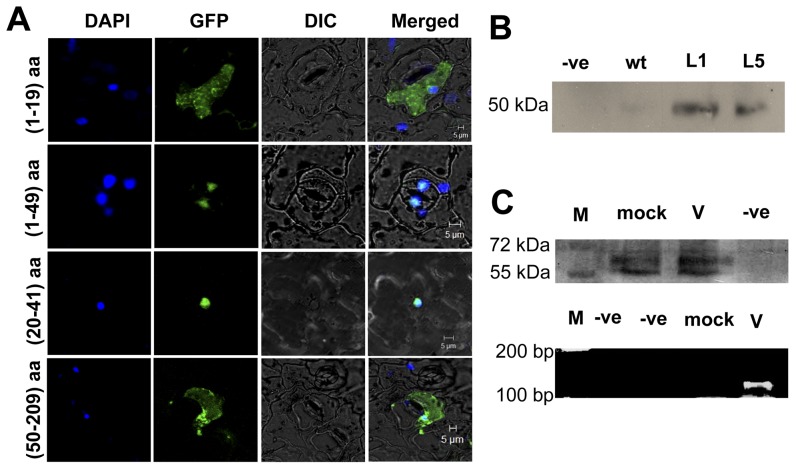
Figure 7. Detection of nuclear localization signal (NLS) in p23 of HCRSV.
(A) DAPI stained nuclei (blue-color foci) were superimposed onto the differential interference contrast (DIC) image to form a merged image. The fragments of GFP fusion proteins pGreen+p23 (1–19 aa)-GFP and pGreen+p23 (50–209 aa)-GFP, which did not contain NLS, were present in the entire cell. The pGreen+p23 (1–49 aa), p23 and p23 (20–41 aa)-GFP, both encompass NLS fragment. GFP signal was mainly present in the nucleus. (B) Wild type (wt) and p23-GFP transgenic Arabidopsis L1 and L5 lines were used as plant materials; anti-GFP antibody was used to carry out co-immunoprecipitation. The pull down protein was probed with anti-importin α antibody. Importin α was detected in the CO-IP samples. (C) Mock and HCRSV-infected kenaf leaves were used for RNA-chromatin immunoprecipitation (CHIP). Before immmunoprecipitation, importin α was detected in sonicated mock and HCRSV-infected kenaf leaves. Truncated p23 (46–183 aa) of HCRSV was detected only in HCRSV-infected leaves using RT-PCR from eluted RNA. M, protein markers.