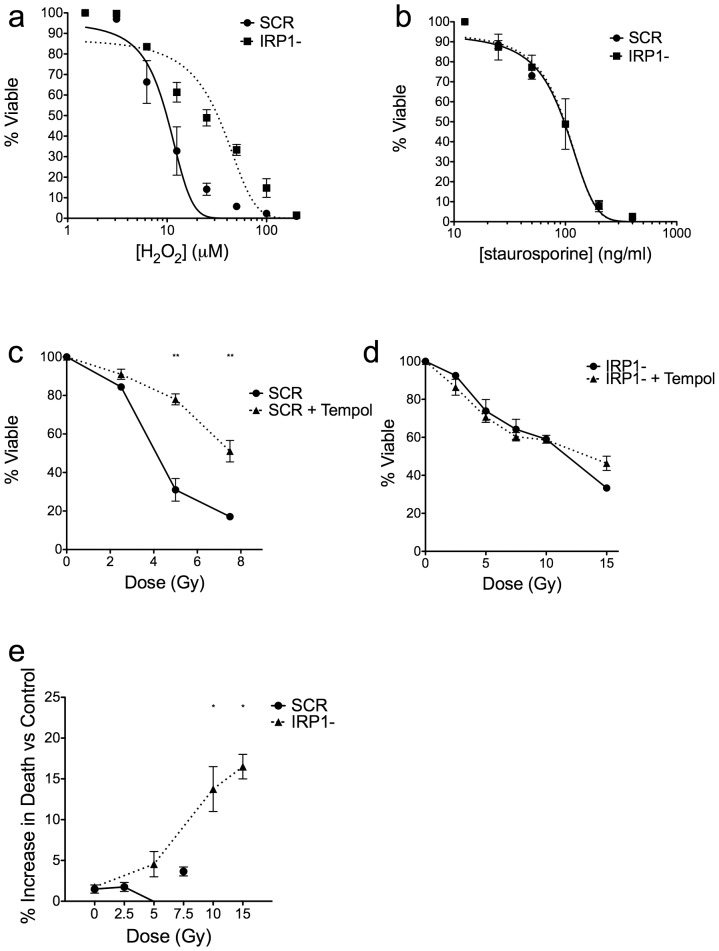
Figure 6. Radioresistance in IRP1- cells is associated with iron availability and a free radical-mediated mechanism.
Panels a–b: IRP1- and control cells were treated with indicated doses of chemicals and assayed for apoptosis by annexin V & PI staining at 24 h post H2O2 treatment (panel a) or 48 h post staurosporine treatment (panel b). Data were fitted to a non-linear variable slope sigmoidal response curve. Panels c–d: cells were treated with 10 mM Tempol for 15 m at 37°C before exposure to indicated doses of gamma rays. Cells were immediately washed and cultured in regular medium for 48 h then assayed for apoptosis by annexin V & PI content. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests was used to measure statistical significance at each dose (** = p<0.01). Panel e: cells were treated with 1 mg/mL of purified human apo-transferrin (control) or transferrin for 6 h in serum-free medium and exposed to equitoxic doses of gamma rays (doses were terminated at 7.5 Gy for control cells because cells were 80% dead or more beyond this dose). Cells were immediately washed and placed in regular culture medium and assayed for apoptosis at 48 h by annexin V & PI content. Data were normalized to viability from apo-tansferrin treated cells and analyzed for significance at equitoxic IR doses using a two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests (* = p<0.05). All data are mean +/− SEM from three independent experiments.