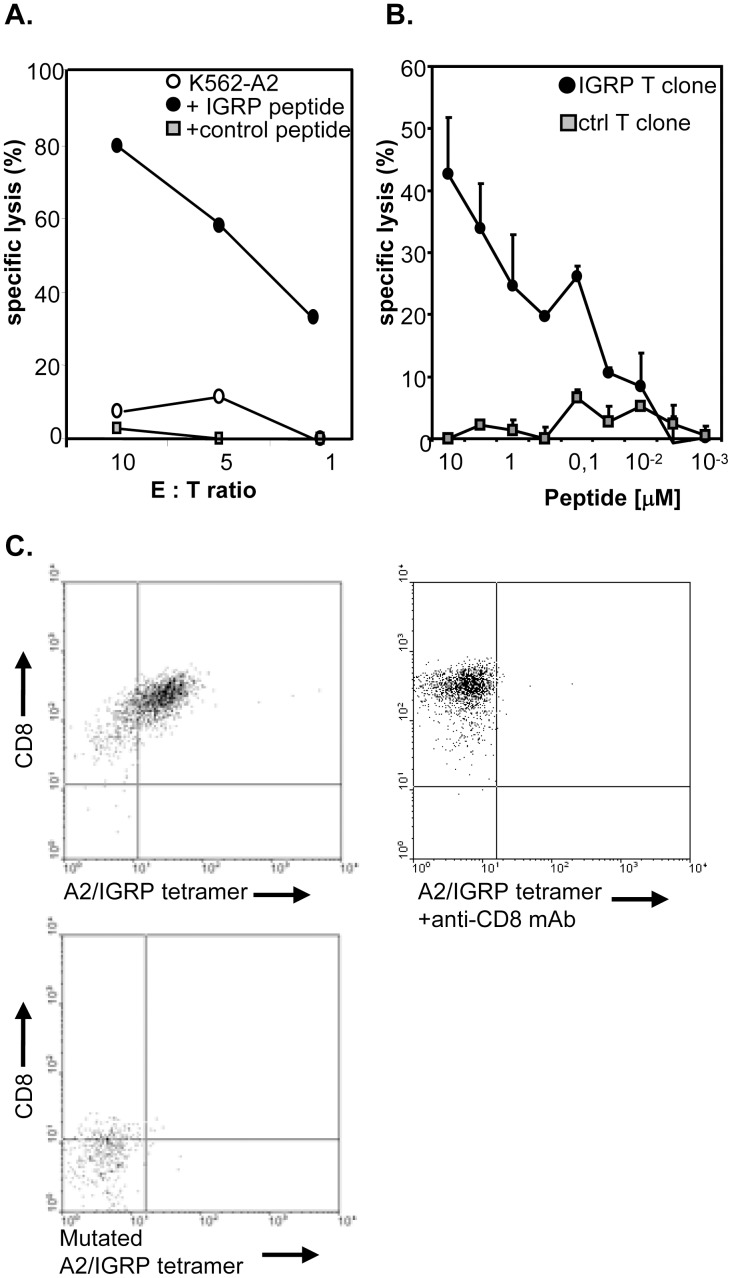
Figure 2. Low-avidity IGRP-specific T-cells exhibit lytic activity in-vitro.
A, Lytic capacity of the IGRP-specific T-cell was examined in a standard 4 h cytotoxicity assay. 3000 51Cr labeled HLA-A2+ IGRP- (black dots), control-(grey squares) or non-peptide (white dots) pulsed targets were incubated with the IGRP-specific T-cells at the indicated ratios. B, Avidity of the IGRP-specific T-cells was examined by titrating the amount of specific (black dots) or control peptide (grey squares) on peptide-pulsed HLA-A2+ target cells. C, Tetramer staining in the presence of anti-CD8 antibody. IGRP-specific CTLs were tested 15 days after the last antigenic stimulation. Cells were labelled with A2/IGRP tetramer in the absence (left plot) or presence of an anti-CD8 antibody (1 µg/ml of SK1; BD Biosciences; middle plot), or T-cells were incubated with a mutated IGRP/A2 tetramer (right plot). After tetramer labelling T-cells were stained with anti-CD8 and expression was analysed by flow cytometry. Examples shown are representative of 3 independent experiments.