Figure 4. NF-1C2 regulation of the CYP11A1 promoter in theca cells.
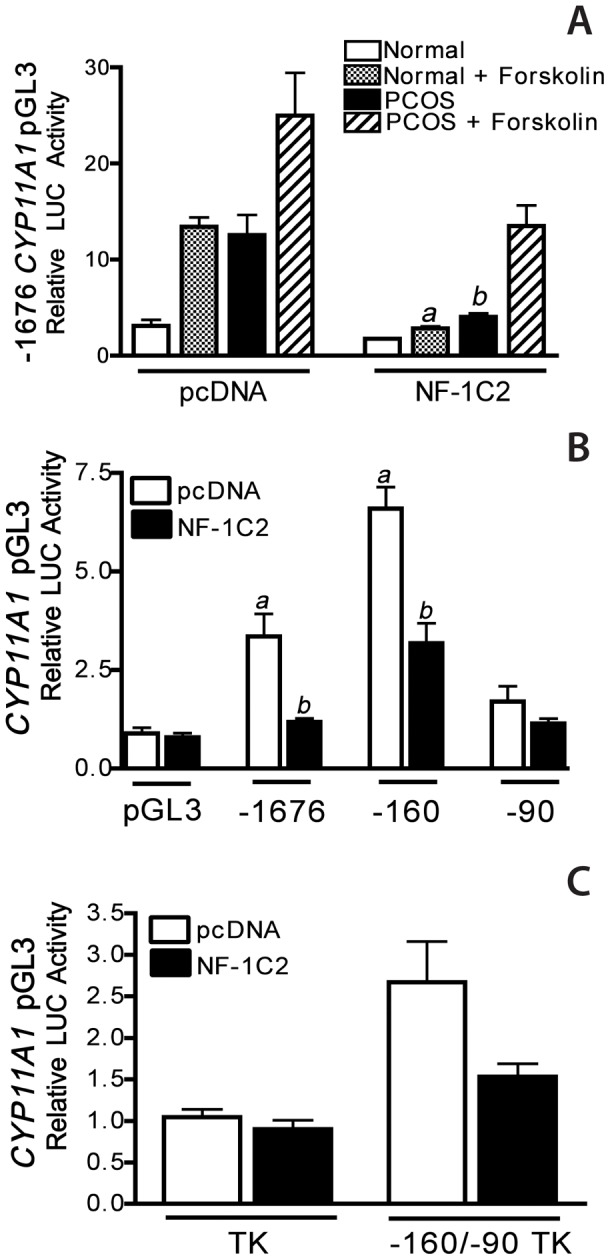
A) The effect of human NF-1C2 on CYP11A1 promoter function was examined in normal and PCOS theca cells transiently transfected with the −1676 CYP11A1 luciferase construct and co-transfected with an empty pcDNA plasmid, or a pcDNA plasmid expressing NF-1C2. Following transfection, cells were cultured in transfection medium with and without 20 µM forskolin (F) for 48 h. To determine the sequences in the CYP11A1 promoter that confer NF-1C2 regulation, cells were transfected with a B) pGL3 constructs containing −1676, −160, or −90 to +49 bp of the 5′-flanking sequence of the CYP11A1 gene, or C) the minimal −160/−90 TK and empty TK constructs, following co-transfection with pcDNA plasmid expressing NF-1C2 or an empty pcDNA plasmid, the cells were cultured in serum free medium for 48 h. All data are presented as relative luciferase (LUC) activity that was normalized with β-galactosidase activity and represent the mean ± SEM of multiple independent experiments. These experiments demonstrate that NF-1C2 inhibits both basal (a, P<0.01) and forskolin (b, P<0.01) stimulated −1676 CYP11A1 promoter function in normal and PCOS theca cells, as well as basal −160 CYP11A1 promoter function (a, P<0.01) in PCOS theca cells. Moreover, sequences between −160/−90 bp of the CYP11A1 promoter confer NF-1C2 inhibition.
