Figure 6. The 5′UTR of CYP11A1 mRNA confers increased stability in PCOS theca cells under basal conditions.
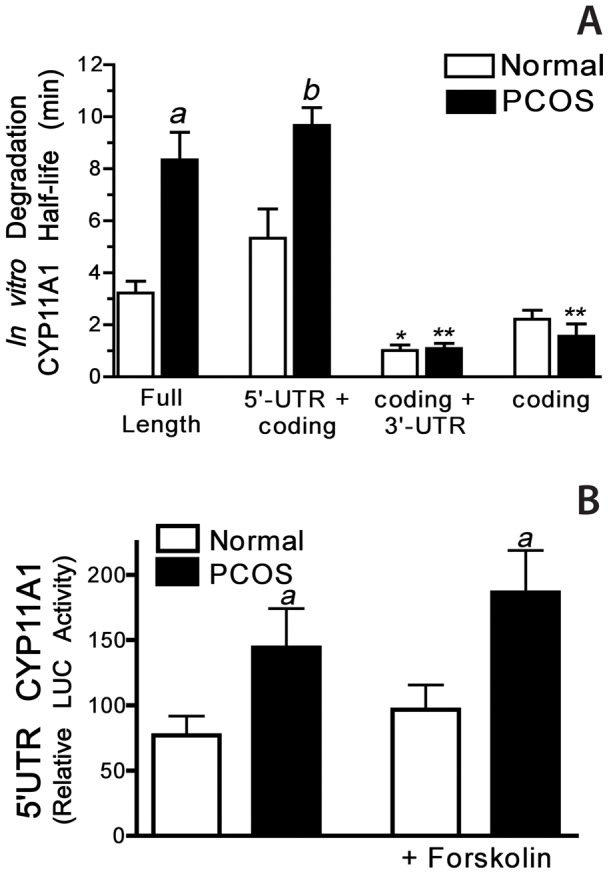
A) The individual half-lives of various CYP11A1 RNA probes were determined using RNA in vitro degradation assays. Biotinylated CYP11A1 mRNA transcripts (i.e., the full-length transcript, 5′UTR+coding region, coding region alone, and coding region +3′UTR) were incubated with cytoplasmic extracts isolated from either normal or PCOS theca cells. The stability of each transcript over time (half-life) is presented as the mean ± SEM of five independent assays. The results of these experiments demonstrated that the stability of CYP11A1 RNA transcripts containing either the full-length (a, P<0.01) or 5′+coding region (b, P<0.01), were significantly increased in assays using PCOS extracts, compared with normal extracts. The coding transcript+3′-UTR was markedly reduced in normal (*, P<0.01) and PCOS (**, P<0.01) theca cells as compared to the 5′UTR+coding transcript, and were similar in normal and PCOS cells. B) To examine functional differences in 5′UTR of CYP11A1 in normal and PCOS theca cells, both cell types were transiently transfected with a luciferase (LUC) construct containing the 5′ UTR of CYP11A1 mRNA and incubated in the absence (untreated) or presence of forskolin (20 µM) for 48 h. Data are presented as relative luciferase (LUC) activity following normalization by ß-galactosidase and represent the mean ± SEM from transfections performed in triplicate in 4 independent normal and 4 independent PCOS theca cells cultures. Luciferase expression of the 5′ UTR construct was significantly higher in PCOS theca cells as compared to normal cells (a, P<0.05). Forskolin treatment had no effect on CYP11A1 stability in normal or PCOS theca cells.
