FIGURE 1.
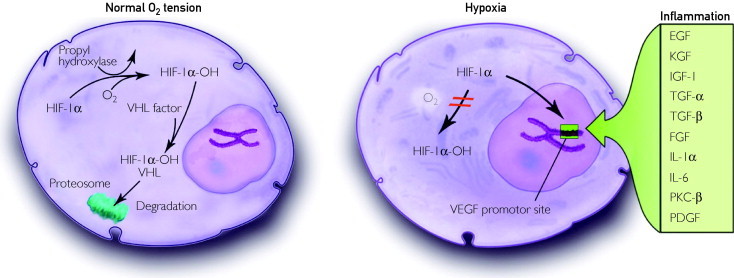
Under conditions of normal oxygen tension (left), HIF-1α undergoes hydroxylation, binds to the VHF, and undergoes degradation within proteosomes. When tissues experience localized hypoxia or inflammation (right), HIF-1α stabilizes and binds to the promoter site of the VEGF gene, thereby increasing VEGF synthesis. EGF = epidermal growth factor; FGF = fibroblast growth factor; HIF-1α = hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; IGF-1 = insulin-like growth factor 1; IL = interleukin; KGF = keratinocyte growth factor; O2 = oxygen; PDGF = platelet-derived growth factor; PKC-β = protein kinase C-β; TGF = transforming growth factor; VEGF = vascular endothelial growth factor; VHF = von Hippel-Lindau factor.
