FIGURE 2.
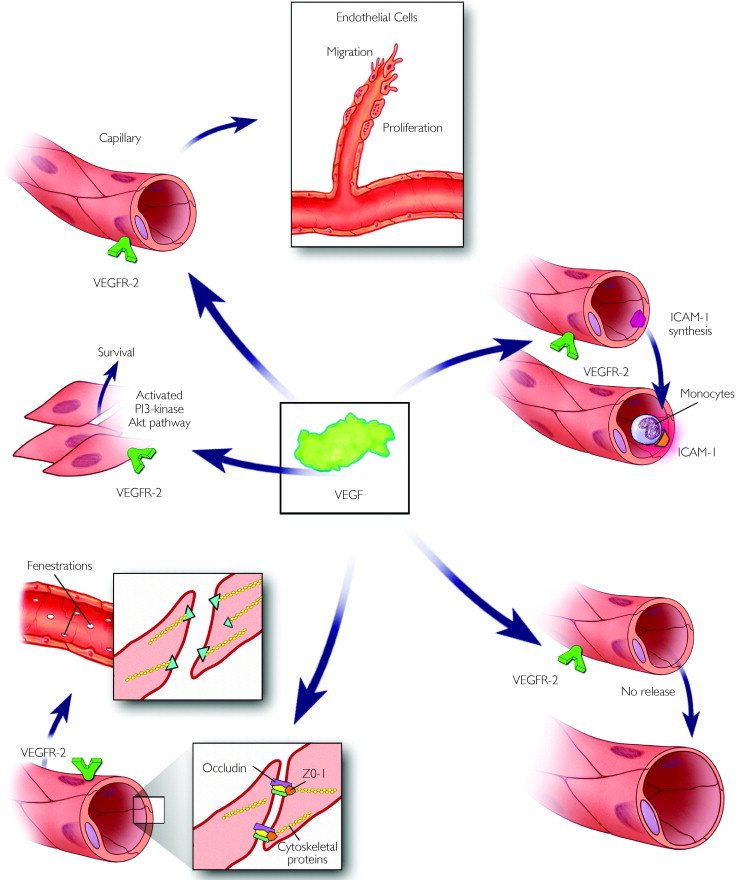
The primary site of VEGF action is vascular endothelium. In response to VEGF, endothelial cells proliferate and migrate; locally release nitric oxide, which causes vasodilation; and increase capillary permeability by creating cellular fenestrations and decreasing the integrity of tight junctions by phosphorylating intracellular and extracellular proteins. ICAM-1 = intercellular adhesion molecule 1; No = nitric oxide; Pl = phosphatidylinositol; VEGF = vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR-2 = vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2; ZO = zonula occludins.
