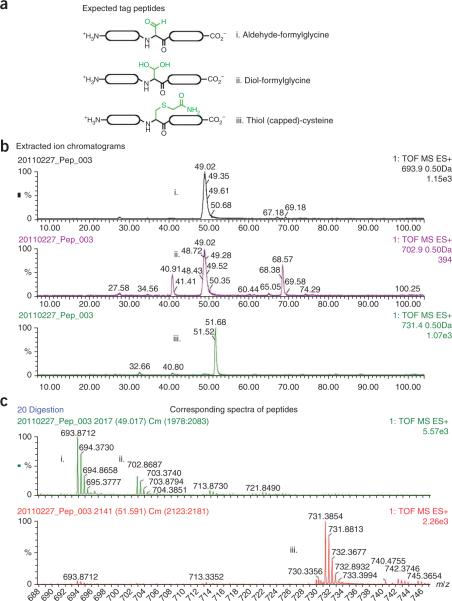
Figure 2.
Anticipated results of LC-MS analysis of tryptic peptides from an aldehyde-tagged protein. Protein was reduced with DTT, alkylated with IAA and digested with trypsin. The sample was analyzed by LC-MS on a Waters QToF mass spectrometer. (a) Expected tag peptides. To determine conversion rates, we monitored the presence of ions corresponding to the peptides containing the formylglycine modification as the aldehyde (i) or the diol (ii) or the unconverted peptide with the Cys protected with iodoacetamide (iii). (b) Illustration of extracted ion currents (XIC) corresponding to the peptides indicated: (i), M + 2H at m/z 693.9; (ii), M + 2H at m/z 702.9; and (iii), M + 2H at m/z 731.4. Note that the carbamidomethylated Cys-containing peptide elutes slightly later than its aldehyde-containing counterpart. (c) Shows mass spectra of the same peptides. The area under the curve (AUC) of the relevant XICs was used to determine the conversion rates as follows: i + ii/i + ii + iii.