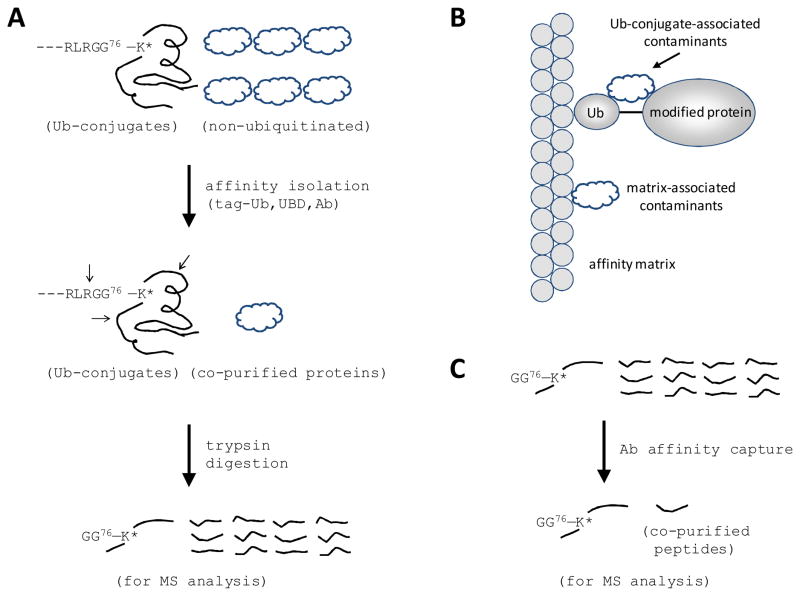
Figure 2.
Strategies for isolating ubiquitinated proteins/peptides from complex mixtures. (A) Schematic representation of the purification strategies based on tagged Ub (e.g. HA, FLAG, His and biotin), Ubiquitin-binding domains (UBDs) or Ub antibodies (Ab). Arrows indicate tryptic sites surrounding a lysine modification residue in Ub-conjugates. Digestion of the Ub moiety generates a small Gly-Gly tag on the lysine residue. (B) Purified Ub-conjugate samples contain 2 classes of contaminated proteins that are not ubiquitinated, one class associated with affinity matrix nonspecifically and the other class interacting more specifically with Ub-conjugates. (C) Immunocapture of GG-tagged peptides to enhance the capacity for identifying ubiquitination sites.