Figure 4.
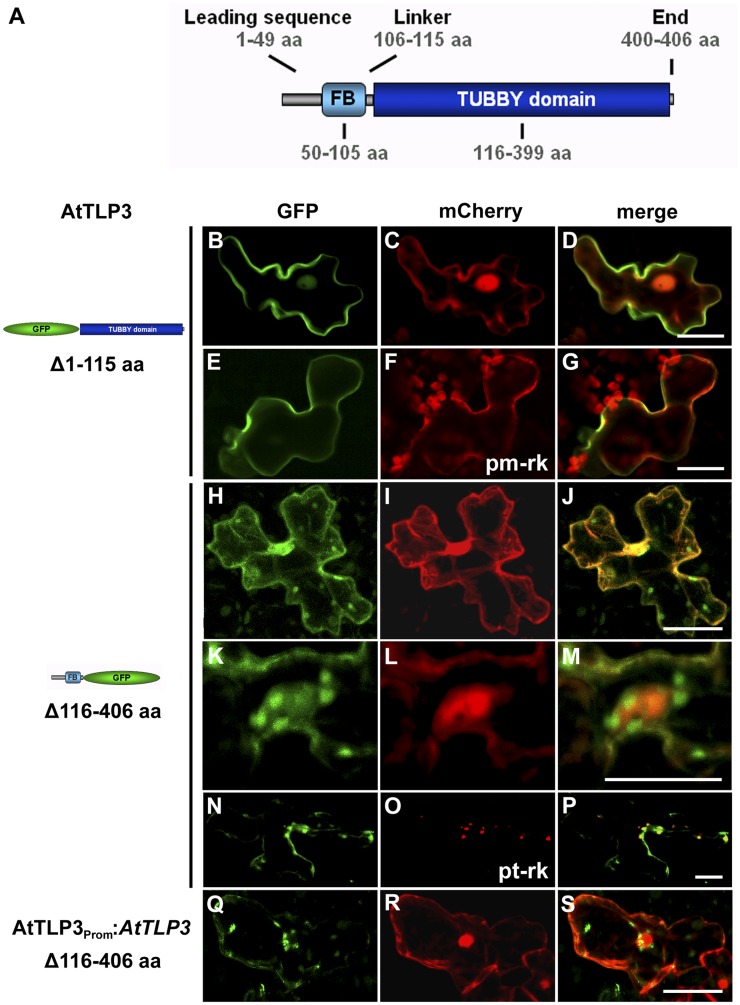
Subcellular localization of the FB and Tubby domains of AtTLP3. A, Model of AtTLP3 with the N-terminal FB domain and the C-terminal Tubby domain. Numbers indicate the lengths and positions of domains within AtTLP3 in amino acids (aa). For all experiments below, leaf cells were cotransformed with the GFP-CT-AtTLP3 (Δ1–115) (B and E) or NT-AtTLP3-GFP (Δ116–406) (H, K, and N) fusions under the control of the 35S promoter (B–P) or the native promoter (Q) and cytosolic and nucleoplasmic marker mCherry (C, I, L, and R), PM marker pm-rk (F), or plastidial marker pt-rk (O) by biolistic transformation. D, G, J, M, P, and S are merged images indicating the subcellular localization of domains. Yellow color indicates the colocalization of green- and red-fluorescing proteins. Constructs used for transformation are indicated on the left. B to D, PM localization of GFP-CT-AtTLP3. E to G, GFP-CT-AtTLP3 colocalizes with the PM marker pm-rk at the PM. H to S, Plastidial and nucleocytosolic localization of NT-AtTLP3-GFP. K to M, Accumulation of plastids around the nucleus in a cell expressing NT-AtTLP3-GFP. N to P, Plastidial localization was confirmed by cotransformation of the NT-AtTLP3-GFP fusion with the plastidial marker pt-rk. Q to S, Cells transformed with NT-AtTLP3-GFP under the control of its endogenous promoter (AtTLP3PROM) also showed plastidial, cytosolic, and nucleoplasmic localization. Bars = 20 µm.