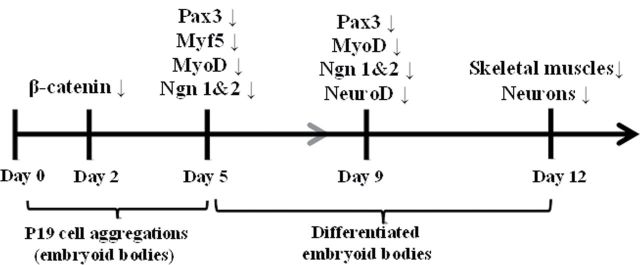
FIG. 7.
Model of the transcription factor cascade that inhibits skeletal myotube and sensory neuron formation after arsenite exposure. During P19 aggregation, β-catenin expression was repressed by arsenic exposure on day 2. The repressed β-catenin leads to the reduction of Pax3, which plays an important role in specification of muscle and neuronal precursors. Pax3 regulates Myf5, MyoD, neurogenin 1, and neurogenin 2, all of which were down-regulated by arsenite exposure expression on day 5 and day 9. The expression of myogenin and NeuroD, which regulate terminal skeletal and neuronal differentiation, was reduced by arsenic on day 9, which therefore leads to the suppressed formation of skeletal muscles and neurons on day 12.