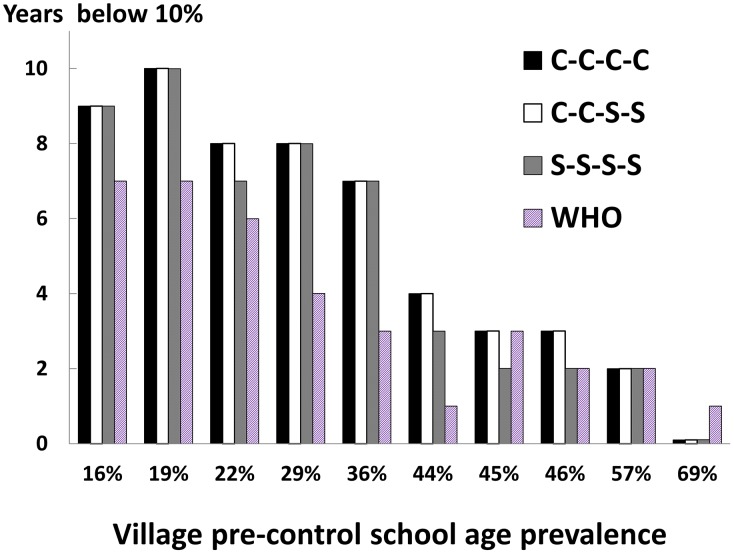
Figure 8. Likely impact of different SCORE strategies on long-term suppression of village prevalence of Schistosoma infection.
As in Figure 6, we simulated the duration of long term post-control suppression of Schistosoma infection to safer levels below 10%. In this case, overall school age adherence was estimated at 70%, and comparisons were made between the 3 most successful four-year SCORE strategies, and standard implementation of the WHO strategy (which takes 6 years to achieve area control). The more aggressive, every-year SCORE strategies resulted in more prolonged post-treatment suppression of infection prevalence than the WHO protocols (in which some communities get assigned to every-other-year treatment). This was apparent in the six villages with the lowest pre-treatment prevalences (16–44%). In the villages with highest pre-intervention levels of infection (57–69%), all of the strategies were very limited in their ability to effect post-treatment suppression (0 to 2 years only).