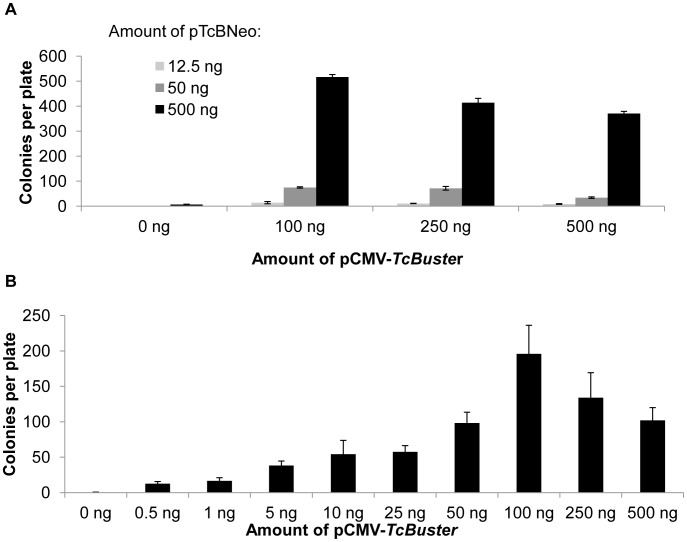
Figure 2. The effect of transposon and transposase plasmid dose on the number of drug-resistant colonies formed.
(a) HEK-293 cells in 6-well plates were transfected in triplicate with either 12.5 ng (light grey bars), 50 ng (dark grey bars), or 500 ng (black bars) of pTcBNeo carrying the neomycin-resistance transposon and 0 ng, 100 ng, 250 ng, or 500 ng of pCMV-TcBuster expressing the transposase. (b) HEK-293 cells in 6-well plates were transfected in triplicate with 500 ng of pTcBNeo plasmid carrying the neomycin-resistance transposon and the indicated amount of pCMV-TcBuster (0.5 ng, 1 ng, 5 ng, 10 ng, 25 ng, 50 ng, 100 ng, 250 ng, or 500 ng). In both a and b, pUC19 was used as filler DNA to increase the total amount of DNA transfected to 1 µg. Cells were diluted 1∶750 in selection media and grown for two weeks to allow drug-resistant cells to multiply and form colonies. The colonies were fixed, stained, and counted. The mean and standard error of the mean (SEM; n = 3) are shown.