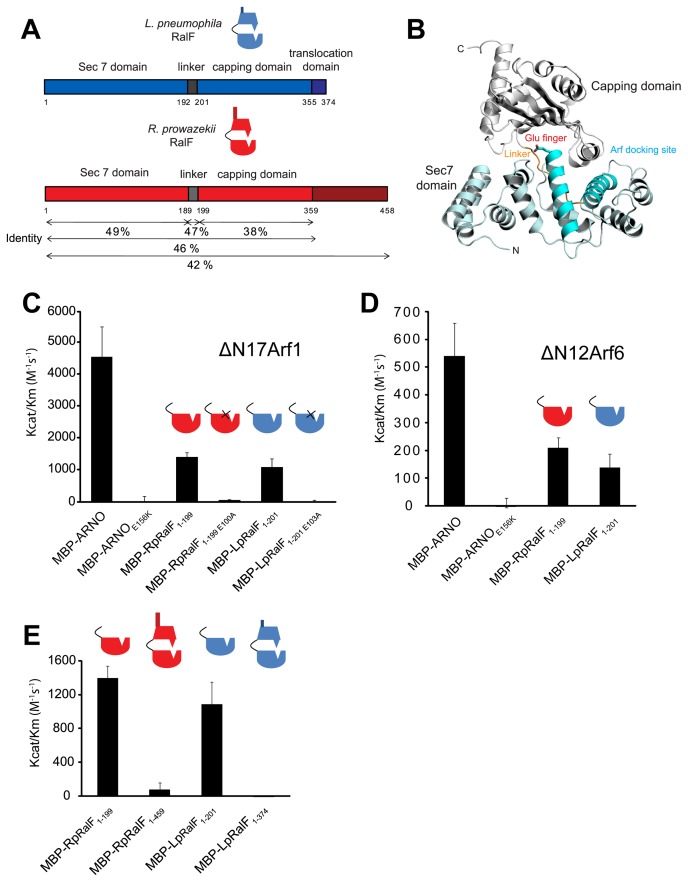
Figure 1. Legionella and Rickettsia RalF proteins are autoinhibited by their capping domain in vitro.
A) Alignment of the Legionella and Rickettsia RalF full length proteins. B) Structural organization of LpRalF protein. Ribbon rendering showing LpRalF Sec7 domain (blue), linker (orange) and capping domain (white) (Protein Data Bank accession code 1XSZ, image generated with PyMOL (http://pymol.sourceforge.net)) [22]. The Sec7 catalytic glutamic acid side chain is represented as a stick with oxygen atoms shown in red. C) LpRalF and RpRalF Sec7 domains activate His-ΔN17Arf1 in vitro. Efficiency of His-ΔN17Arf1 nucleotide exchange catalyzed by the indicated MBP-tagged proteins. Kcat/Km values were obtained as described in Materials and Methods. Average and standard deviation are calculated from three independent experiments. D) Efficiency of His-ΔN12Arf6 nucleotide exchange catalyzed by MBP-tagged LpRalF and RpRalF Sec7 domains. Kcat/Km values were obtained as described in Materials and Methods. Average and standard deviation are calculated from three independent experiments. E) The RalF capping domain regulates GEF activity. Comparison of Kcat/Km values for His-ΔN17Arf1 nucleotide exchanged catalyzed by the Sec7 domain and the full length RalF proteins. Average and standard deviation are calculated from three independent experiments.