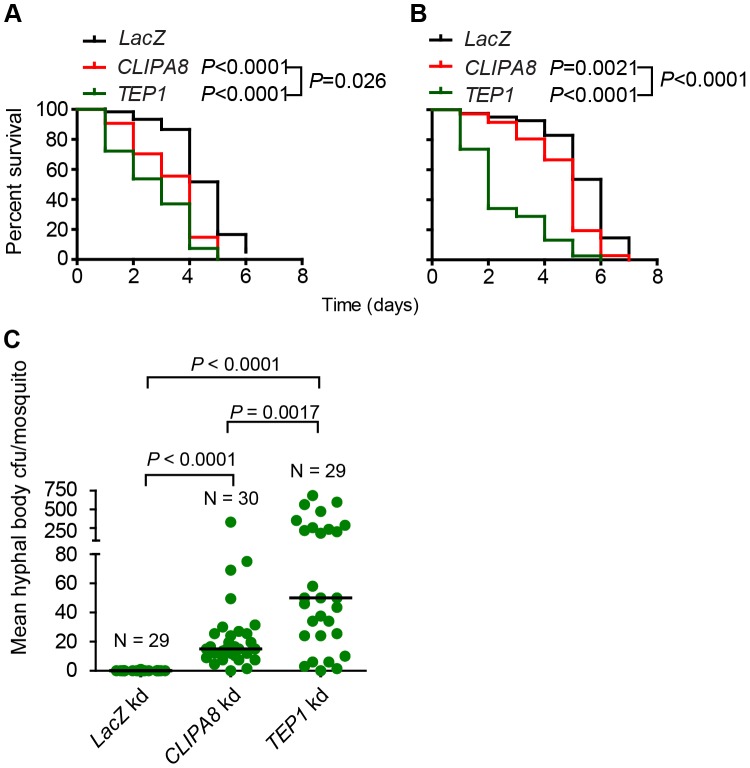
Figure 7. CLIPA8 and TEP1 kd mosquitoes are more sensitive to B. bassiana infections.
LacZ, TEP1 and CLIPA8 kd adult female A. gambiae mosquitoes were challenged with B. bassiana (strain 80.2) either by (A) bringing the mosquitoes in contact with a lawn of conidia on fungal PDA plates or (B) by spraying mosquitoes with a suspension of 1×108 conidia/ml. Dead mosquitoes were counted daily over the indicated period. Graphs represent percent survival as calculated by the Kaplan-Meier method for one representative experiment of each treatment. Statistical significance was calculated by the log rank test. Survival curves were considered to be significantly different if P<0.05. (C) B. bassiana infected CLIPA8 and TEP1 kd mosquitoes contained significantly more hyphal body colony forming units (cfu) than infected LacZ kd controls. Here, mosquitoes were challenged by spraying with B. bassiana strain 80.2 at a suspension of 5×107 conidia/ml and batches of two mosquitoes each were collected four days later, surface sterilized, grinded and serial dilutions plated on B. bassiana selective medium. Each circle represents mean hyphal body cfu per mosquito per batch. Medians are indicated with horizontal lines and were 0, 15 and 50 for LacZ, CLIPA8 and TEP1 kd mosquitoes, respectively. The numbers of batches (N) processed per genotype are indicated. Statistical significance was calculated using the Mann-Whitney test; medians were considered significant if P<0.05. Results are from two independent biological experiments involving different batches of mosquitoes and fungal conidia.